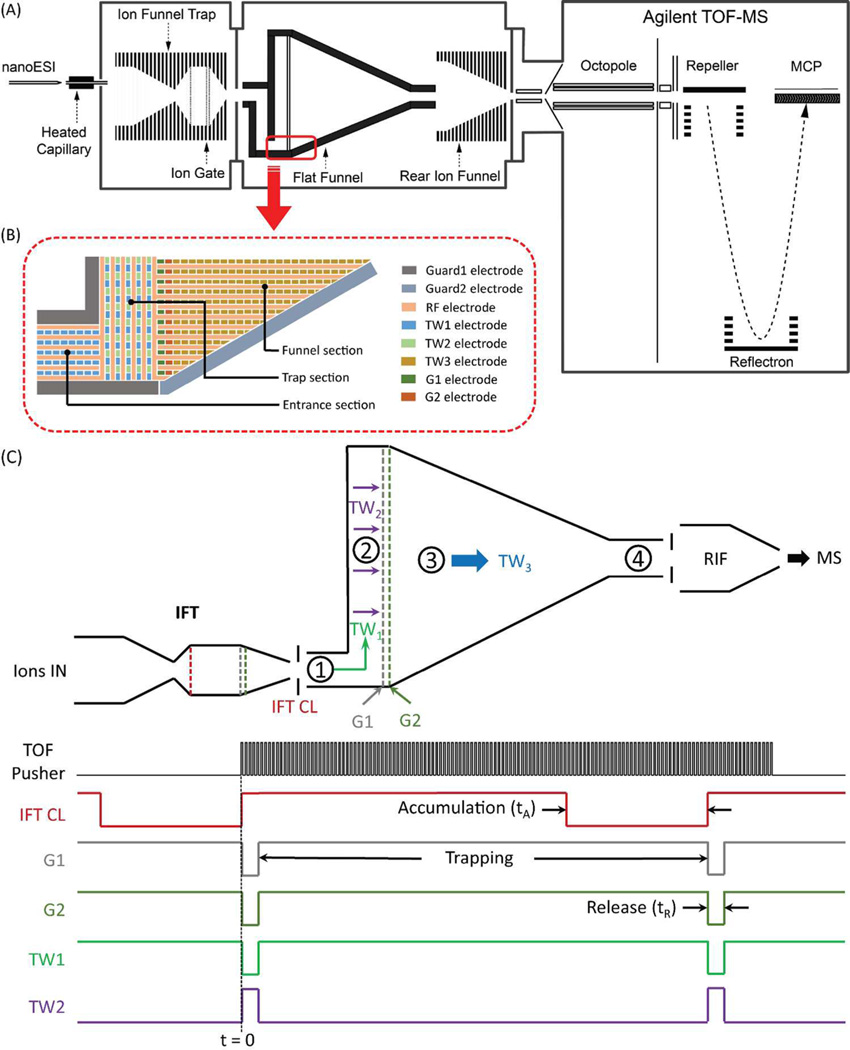
Figure 1.
(A) Representative schematic of the TW SLIM FF IM-MS instrument used in this work; (B) schematic of the TW SLIM FF intersection region showing the electrode arrangements of rf, TW, guard electrodes in different sections and dual gate (G1, G2) electrodes; (C) schematic diagram of TW SLIM FF (the numbers refer to the different sections (see text)) and IFT (it works in continuous mode and IFT CL is used to inject ions into TW SLIM FF as an entrance gate), and the pulse sequence and voltage profiles for ion accumulation and ejection. (All voltages were controlled using the same digital TTL signal. When it was high (ion filling), IFT CL was open, G1 and G2 were close, TW1 was on and TW2 was off; while it was low (ion ejection), IFT CL was close, G1 and G2 were open, TW1 was off but TW2 was on).