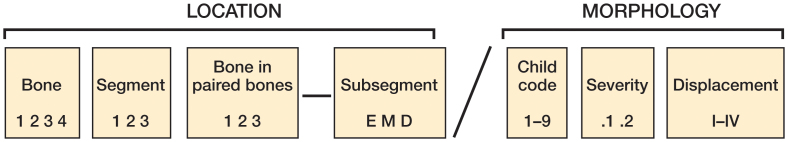
Figure 1.
Overall structure of the AO Pediatric Comprehensive Classification of Long Bone Fractures (AO PCCF). Fracture location is identified by the fractured long bone (1 = humerus, 2 = radius/ulna, 3 = femur, and 4 = tibia/fibula) and its injured segments (1 = proximal, 2 = shaft, 3 = distal). If only a single bone of the forearm or the lower leg is fractured, a small letter, describing the bone ("r", "u", "t", or "f") is added after the segment code. The capital letter that follows identifies the fracture type as epiphyseal (E) or metaphyseal (M) for proximal or distal fractures, or diaphyseal (D) for shaft fractures. Fracture morphology is identified by a code for specific child patterns related to the fracture type, a severity code (occurrence of multifragmentation, distinguishing between simple and wedge or complex fractures), and—if required—an additional displacement code for supracondylar or radial head fractures.