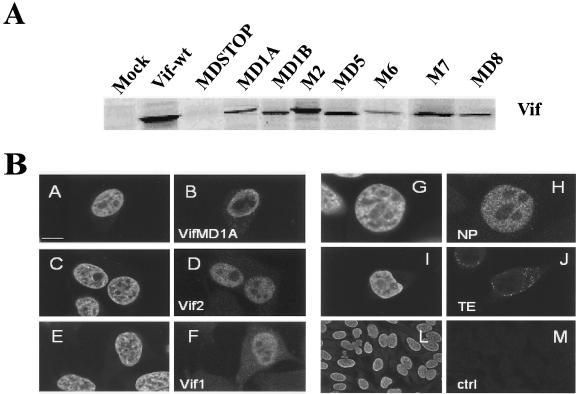
FIG. 3.
(A) Analysis of in vitro transcription-translation products with different DNA constructs encoding Vif2 wild-type and Vif2 mutant proteins. The results show that Vif2 mutant proteins are expressed with molecular weights similar to those of the wild-type protein. Nevertheless, an increased mobility is noted for deletion mutants. As expected, when vif-containing stop codon (MDSTOP) was used no protein was expressed. (B) Cellular localization of Vif2 mutants by using immunolabeling detection. HeLa cells were transfected with Vif2 and Vif1 wild-type and Vif2 mutant constructs cloned in fusion with HA epitope at the N terminus. Cells were fixed 18 h posttransfection, and detection was performed by indirect immunofluorescence. Nucleic acids were counterstained with TOTO-3 (in subpanels A, C, E, G, I, and L). The results show the expression of HA-Vif2 MD1A (subpanel B) and wild-type HA-Vif2 and HA-Vif1 (subpanels D and F) in the nucleus. Positive controls for nuclear localization NP (subpanel H) and cytoplasmic localization TE (subpanel J) were used. Nontransfected cells (subpanels L and M) show no background staining or nonspecific reactivity from the antibodies. Equatorial optical sections were collected on a confocal laser-scanning microscope. Bars, 10 μm.