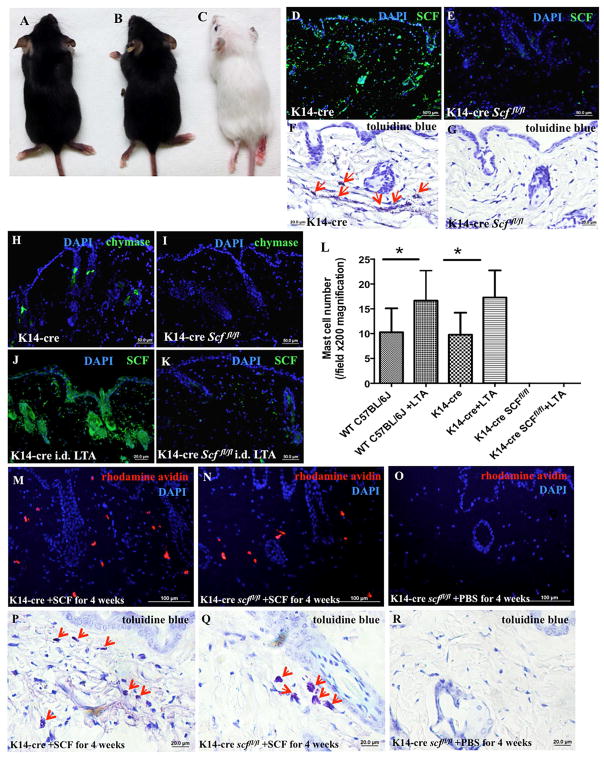
Figure 5. K14-cre Scffl/fl mice lack SCF in the epidermis and MCs in the dermis.
(A–C) K14-cre (A) and Scffl/fl mice (B) exhibit a normal phenotype, while K14-cre Scffl/fl mice are albino (C); (D–E) K14-cre (D) and K14-cre Scffl/fl (E) mouse skin was immunostained with anti-SCF monoclonal antibody (green) and DAPI (blue); (F–G) Toluidine blue staining of the skins of K14-cre (F) and K14-cre Scffl/fl mice (G), red arrows indicate MCs; (H–I) Skins from K14-cre (H) and K14-cre Scffl/fl (I) mice were immunostained with anti-chymase monoclonal antibody (green) and DAPI (blue); (J–K) Following 100 μl LTA (1 mg/ml) injection, K14-cre (J) and K14-cre Scffl/fl (K) mouse skins were immunostained with anti-SCF monoclonal antibody (green) and DAPI (blue); (L) Quantification of MC numbers by positive toluidine blue staining shows that MC presence could not be rescued by LTA when SCF was conditionally deleted from skin epidermis (*p<0.05). (M–O) Rhodamine-avidin staining (red) and DAPI (blue) for MCs in the skins of K14-cre (M) and K14-cre Scffl/fl mice (N) subcutaneously injected with SCF (50 μg/kg/day) or PBS (O) for 4 weeks; (P–R) Toluidine blue staining for MCs (red arrows indicate MCs) in the skins of K14-cre (P) and K14-cre Scffl/fl mice (Q) subcutaneously injected with SCF (50 μg/kg/day) or PBS (R) for 4 weeks.