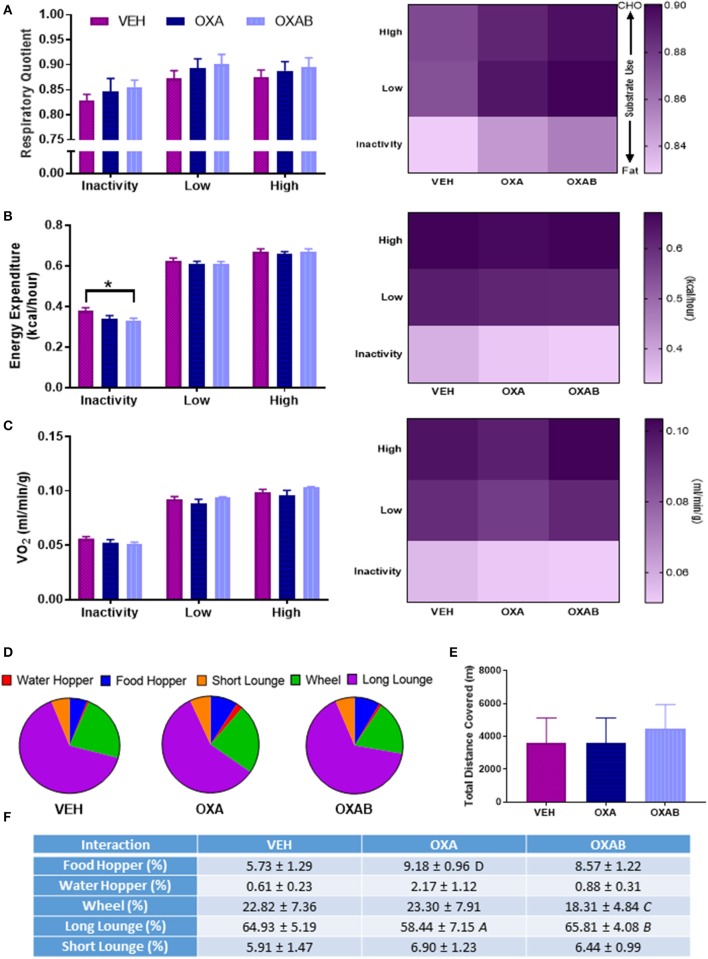
Figure 3.
BGP-15 reduces basal energy expenditure with OXA treatment not affecting exercise capacity. (A) There was no significant effect of treatment on the respiratory quotient. (B) Energy expenditure at rest was reduced by BGP-15 adjunct therapy. (C) Oxygen consumption was not effected by treatment. (D,F) Time budgets of activities of daily living: OXA treatment reduced time spent engaged in long lounges (p < 0.05) while OXAB treatment reduced the time spent engaged in voluntary wheel running. (E) There was no effect of treatment on total meters covered (combination of wheel and pedestrian meters). CHO, Carbohydrate; VO2, Volume Oxygen. Table significance: (A) p < 0.05 OXA vs. VEH, (B) p < 0.05 OXA vs. OXAB, (C) trend (p = 0.088) OXA vs. OXAB, (D) trend (p = 0.057) OXA vs. VEH. Significance: *p < 0.05. n = 6–8.