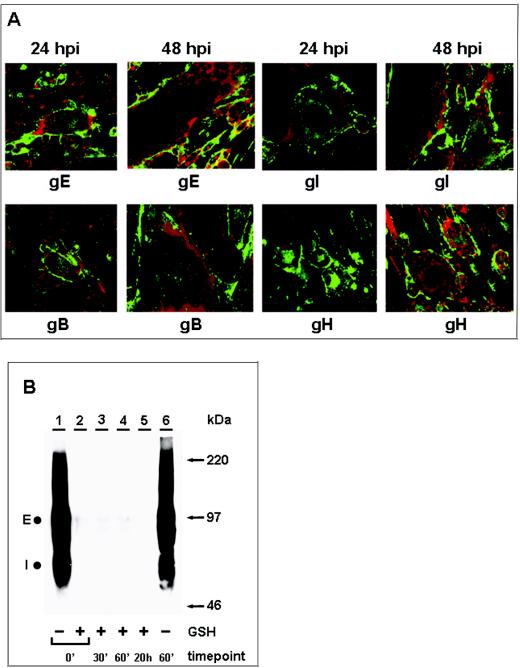
FIG. 1.
Inhibition of VZV glycoprotein endocytosis during late infection. VZV-infected cells were processed for the confocal endocytosis assay as described in the text. (A) Representative micrographs of cultures at 24 and 48 hpi were examined at the 60-min endocytosis time point after labeling was done with a MAb specific for gE, gI, gB, or gH. The postendocytosis localization of VZV glycoproteins was investigated by staining with Alexa 488-fluoroconjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin secondary antibody (green). In contrast to the results obtained at 48 hpi, at 24 hpi labeled glycoproteins were located at the plasma membrane and in vesicles within the cytoplasm of the syncytia. The vesicles were especially evident in smaller syncytia. Nuclei were stained with TOTO-3 (red). (B) Biotin endocytosis assay showing the inhibition of gE internalization at 48 hpi. Cells were infected for 48 h, and samples were processed for the biotin endocytosis assay as described in the text. The numbers below the gel indicate the endocytosis time points at 37°C; + and − above the numbers indicate the presence and absence of GSH treatment, respectively. Samples were separated by SDS-8% PAGE under nonreducing conditions, and internalized biotinylated glycoprotein was detected with Streptavidin-HRP by Western blotting. E and I designate the two glycoproteins. Additional controls for this assay are shown in Fig. 2. The corresponding molecular mass markers are indicated on the right.