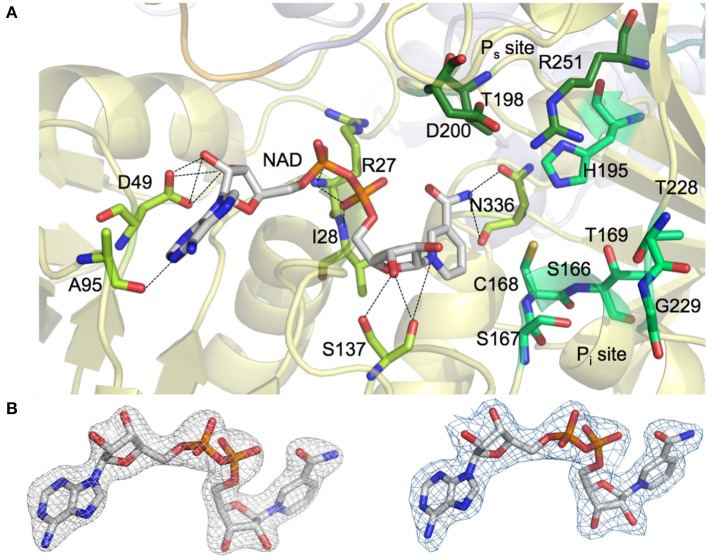
Figure 2.
NAD+ and phosphate binding sites in AvGAPDH. (A) Binding pockets for the NAD+ cofactor (shown in sticks with carbon atoms in gray and all other atoms in CPK colors) and for the inorganic and substrate phosphate sites (“new Pi” and Ps sites, labeled). The placement of the Pi site in AvGAPDH as a “new Pi” site is consistent with the S. aureus GAPDH structure (PDB ID 3K73). Enzyme residues in direct contact with NAD+ are represented in sticks (carbon atoms in light green) and polar interactions (hydrogen bonds) are depicted as dotted lines. Residues predicted to participate in the stabilization of the inorganic and substrate phosphate groups (including the catalytic Cys168) are also shown as sticks (with carbon atoms in two different shades of dark green). The AvGAPDH structural scaffold is shown in ribbons in depth-cued light colors. (B) Omit map showing unbiased electron density map of NAD+ cofactor in AvGAPDH. Unbiased omit map calculated with molecular replacement phases (prior to building the cofactor and solvent structures and prior to refinement) contoured at 1.5 σ revealing the presence of the NAD+ cofactor at full occupancy. For comparison, electron density map for the final model of the NAD+ cofactor displayed at the same contour level (right). The figure was produced with PyMOL (Schrodinger LLC).