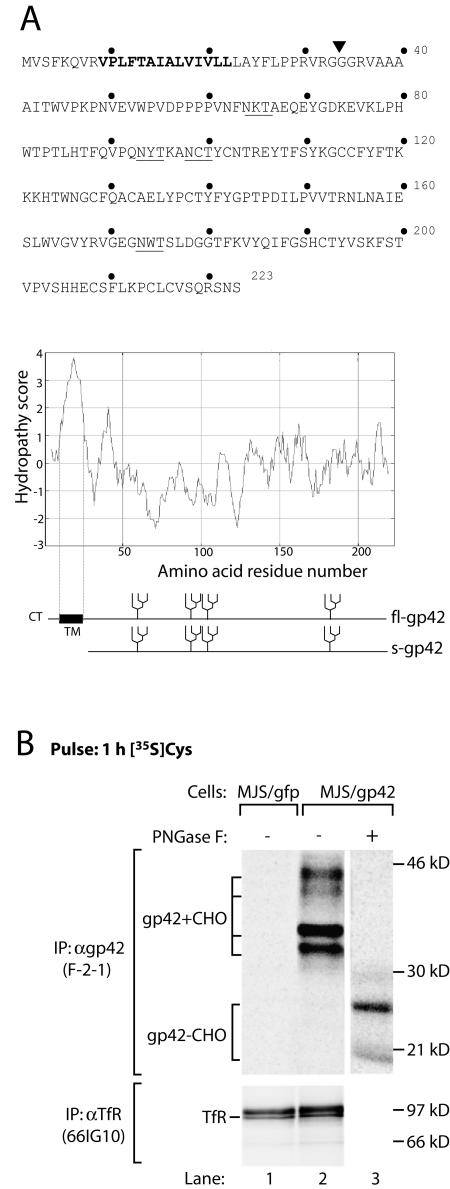
FIG. 1.
EBV gp42 occurs in two forms. (A) Amino acid sequence (single-letter code) and Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot of EBV gp42. Bold type highlights the putative transmembrane domain. The N-linked glycosylation sites are underlined. A signal sequence cleavage site is predicted between residues 33 and 34 (inverted triangle); fl-gp42 and the truncated protein potentially generated upon cleavage (s-gp42) are depicted. CT, cytoplasmic tail; TM, transmembrane domain. (B) MJS/gp42 cells (lanes 2 and 3) and control MJS/gfp cells (lane 1) were metabolically labeled for 1 h with [35S]Cys (gp42) or with[35S]Met (TfR). After lysis of the cells, MAb F-2-1 was used to isolate EBV gp42 molecules. Portions of the immunoprecipitates were treated with PNGase F to remove N-linked glycans. Glycosylated (gp42+CHO) and nonglycosylated (gp42−CHO) gp42 polypeptides are indicated. As a control protein, TfR was precipitated with MAb 66IG10. Samples were analyzed by reducing SDS-12% PAGE. IP, immunoprecipitation; α, anti-.