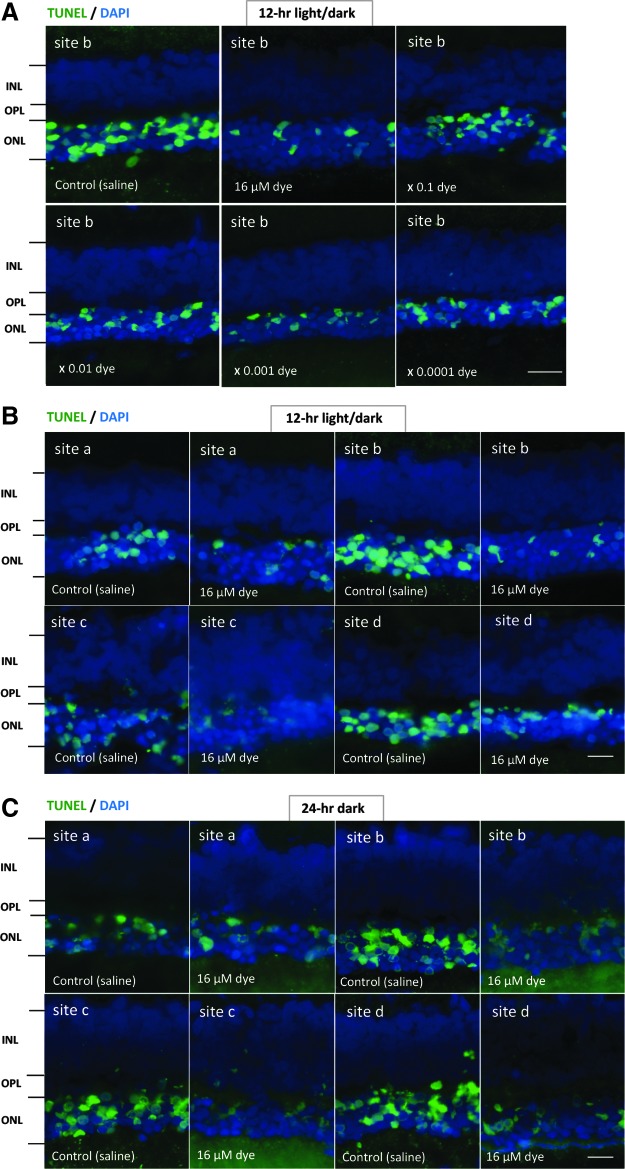
FIG. 2.
The detection of apoptosis in retinal sections of each group of rats. (A) TUNEL staining (green) of retinal sections (site b) of the eyes with intravitreous injection of 3 μL saline in the right eye or series of dilutions of the dye stock solution in the left eye under 12-h light–dark cycle. Eyes were enucleated 2 weeks after the first injection at the age of 4 weeks. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The number of TUNEL-positive cells in the outer nuclear layer (ONL) was less in the dye-injected eyes than in the saline-injected eyes. (B) TUNEL staining of retinal sections at 4 different retinal sites (a, b, c, and d) in the left eye with dye injection (16 μM) compared with that in the right eye with saline injection under 12-h light–dark cycle. (C) TUNEL staining of retinal sections at 4 different retinal sites (a, b, c, and d) in the left eye with dye injection (16 μM) compared with that in the right eye with saline injection under 24-h constant dark condition. INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. Scale bar: 10 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.