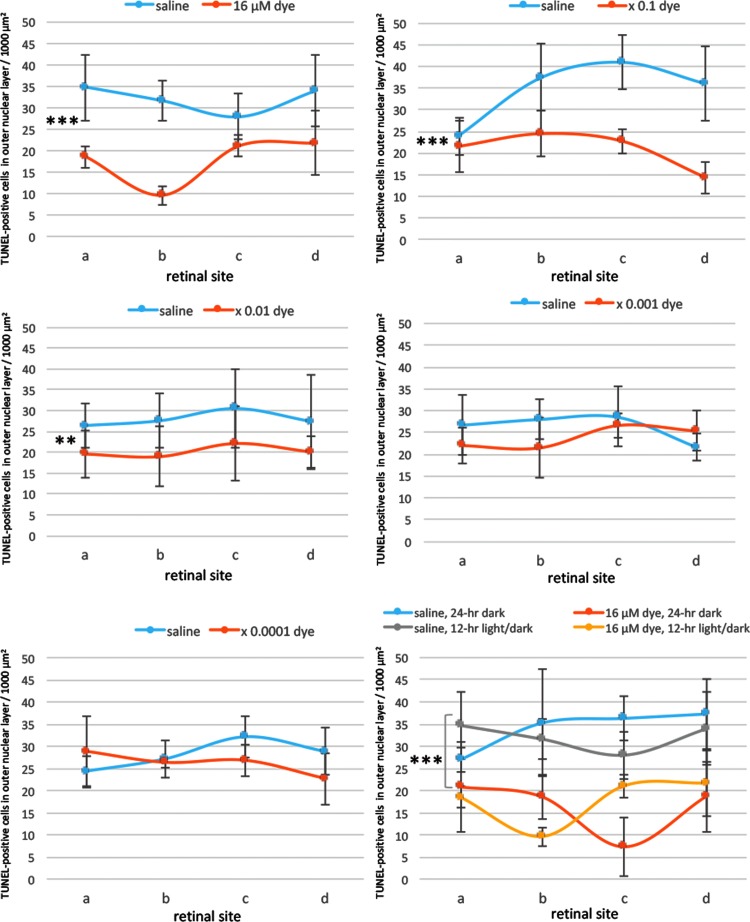
FIG. 3.
Quantitative analysis of apoptotic cells in the ONL of each group of rats. TUNEL-positive cell counts per 1,000 μm2 in the ONL of 4 different retinal sites (a, b, c, and d) of the left eye with dye injection at 5 concentrations compared with those of the right eye with saline injection under 12-h light–dark cycle. TUNEL-positive cell counts were significantly different among different dye concentrations (P = 0.0001), but not significantly different among 4 different retinal sites (P = 0.144, 2-factor analysis of variance [ANOVA]). TUNEL-positive cell counts in dye-injected eyes were significantly less than in saline-injected eyes at the concentration of 16 μM (***P = 0.0001), 16 μM × 0.1 (***P = 0.0001), and 16 μM × 0.01 (**P = 0.002). The bottom right panel shows TUNEL-positive cell counts in the eyes injected with dye (16 μM) versus saline under 12-h light–dark cycle versus under 24-h constant dark condition. There was significant difference between dye-injected eyes and saline-injected eyes under 24-h dark condition (***P = 0.0001). T bars indicate standard deviation.