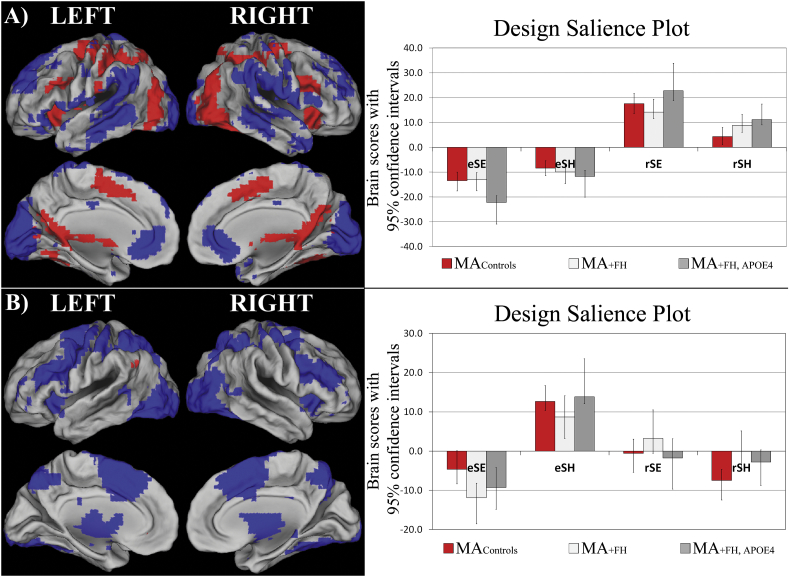
Fig. 1.
T-PLS LV1 and LV2 result. A) The singular image and design salience plot for T-PLS LV1. The singular image is thresholded at a bootstrap ratio of ± 3.5, p < 0.001. Red brain regions reflect positive brain saliences and blue regions reflect negative brain saliences. Activations are presented on template images of the lateral and medial surfaces of the left and right hemispheres of the brain using Caret software (http://brainvis.wustl.edu/wiki/index.php/Caret:Download). The design salience plots represent the brain scores with 95% confidence intervals (y-axis) for each group for each task-type (x-axis). eSE = encoding, easy spatial context memory tasks; eSH = encoding, hard spatial context memory tasks; rSE = retrieval, easy spatial context memory tasks; rSH = retrieval, hard spatial context memory tasks. The design salience plot for T-PLS LV1 indicates this LV identified brain regions that were differentially activated during successful spatial context retrieval (positive saliences) vs. encoding (negative saliences). B) The singular image and design salience plot for T-PLS LV2. The singular image is thresholded at a bootstrap ratio of ± 3.5, p < 0.001. This LV identified brain regions that were differentially activated during hard spatial encoding (eSH; positive saliences) vs. easy spatial encoding (eSE; negative saliences).