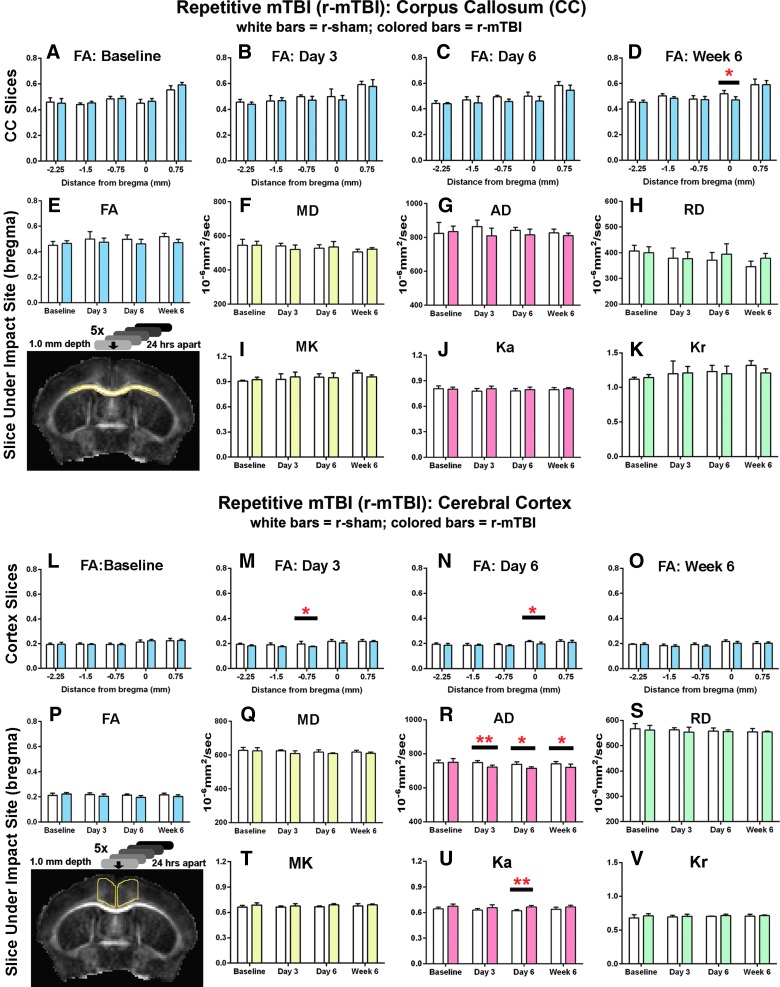
FIG. 3.
Diffusion imaging abnormalities after r-mTBI. Corpus callosum (CC) analysis is shown in upper graphs (A–K), for CC region outlined in yellow on upper image) and medial cerebral cortex values are shown in lower graphs (L–V, for cortical region outlined in yellow on the lower image). Each region is shown at the coronal level containing the anterior commissure, which is under the impact site at bregma. r-sham and r-mTBI mice were scanned as yoked pairs with all mice being scanned at four time points—baseline (BL) and post-injury at 3 days, 6 days, and 6 weeks. Five coronal slices (one rostral to bregma, one at bregma = 0, and 3 caudal to bregma) were analyzed. (A–D) FA values in the CC showing all five coronal slices with locations noted as relative to bregma. A significant reduction in FA was noted in r-mTBI mice only at the bregma level at 6 weeks (D). (E–K) CC values in the individual coronal slice at bregma are shown across time points for the full set of parameters analyzed—diffusion tensor imaging (FA, MD, AD, and RD) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (MK, Ka, and Kr). No parameters show a significant injury effect that reaches significance at any of the post-injury time points. (L–O) Analysis across coronal slices in the medial cortex shows a significant reduction in FA in r-mTBI mice versus sham near the impact site on days 3 and 6 (M and N). (P–S) Analysis of the individual slice under the impact site across time points for all diffusion parameters shows a significant injury effect in the axial dimension for both AD with diffusion tensor imaging (R) and Ka with diffusion kurtosis imaging (U). Values are mean ± standard deviation, n = 6 for each condition at each time point; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. AD, axial diffusivity; FA, fractional anisotropy; Ka, axial kurtosis; Kr, radial kurtosis; MD, mean diffusivity; MK, mean kurtosis; RD, radial diffusivity; r-mTBI, repetitive mild traumatic brain injury; r-sham, repetitive sham.