Figure 5.
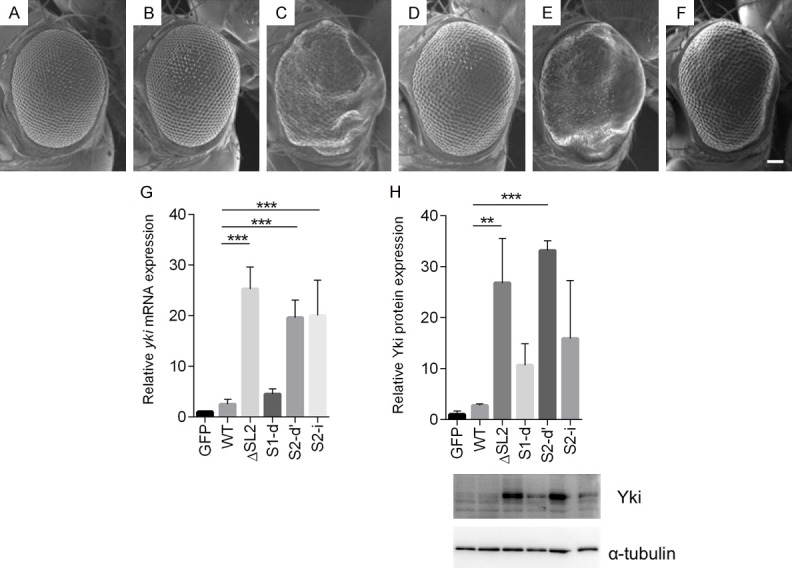
Expression of the ΔSL2 and S2-d yki expression constructs in eye discs induces severe rough eye phenotypes. (A-F) Each panel shows a scanning electron micrograph of an adult compound eye. Scale bar, 66.6 μm. (A) GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-GFP/+; +, (B) GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-FL (8-1-1)/+, (C) GMR-GAL4/UAS-ΔSL2 (20-3-4); +; +, (D) GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-S1-d (20-3-1)/+, (E) GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-S2-d’ (84-1)/+; +, (F) GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-S2-i (13-4)/+, (G) Relative expression levels of yki mRNA in eye imaginal discs, normalised to GAPDH mRNA. Transcripts with a missing or disrupted miR-8 seed sequence over-accumulate (H) Relative Yki protein expression levels normalised to a-tubulin protein expression in eye imaginal discs calculated from Western blots. Level of Yki protein in S2-d or ΔSL2 discs is much higher than controls, while S1-d or S2-i discs yield moderately increases Yki protein expression. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s Multiple comparisons test).
