Figure 5. Model of the CRL4-DCAF1 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Vpr modifies the surface of the common DCAF1 substrate receptor such, that UNG2 or other cellular components can now interact and become a substrate for ubiquitination.
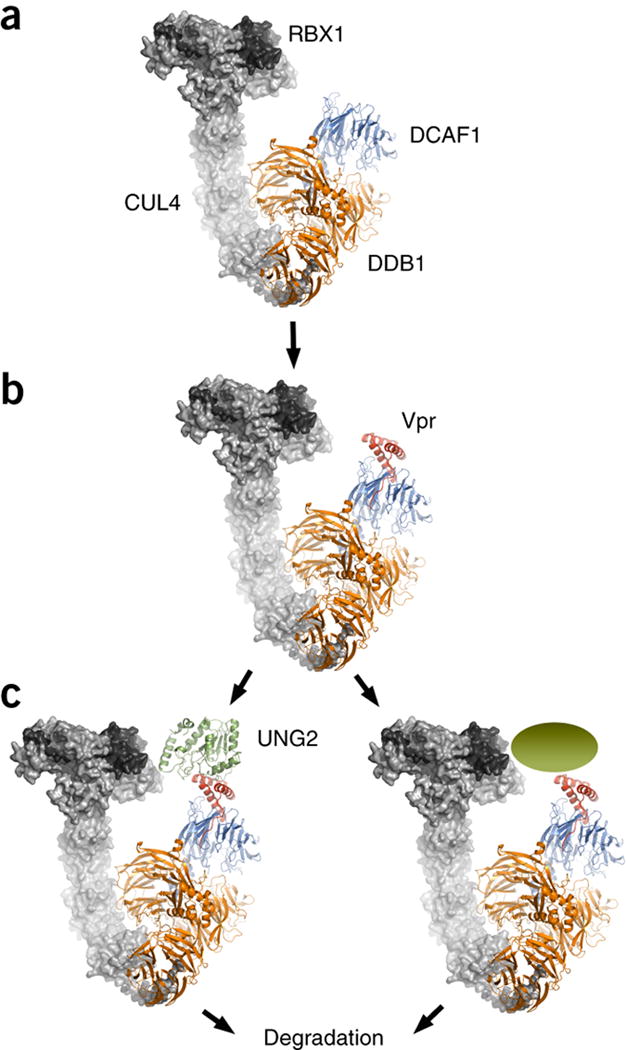
(A) RBX1 and CUL4 in complex with DDB1 (gray surface representation, PDB 2HYE)57 was superimposed on the DDB1 portion of the current DDB1-DCAF1-Vpr-UNG2 complex structure (ribbon representation).
(B) Vpr alters the substrate-binding surface of DCAF1, thereby allowing
(C) Recruitment of UNG2 or other cellular substrates to the E3 ligase for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.
