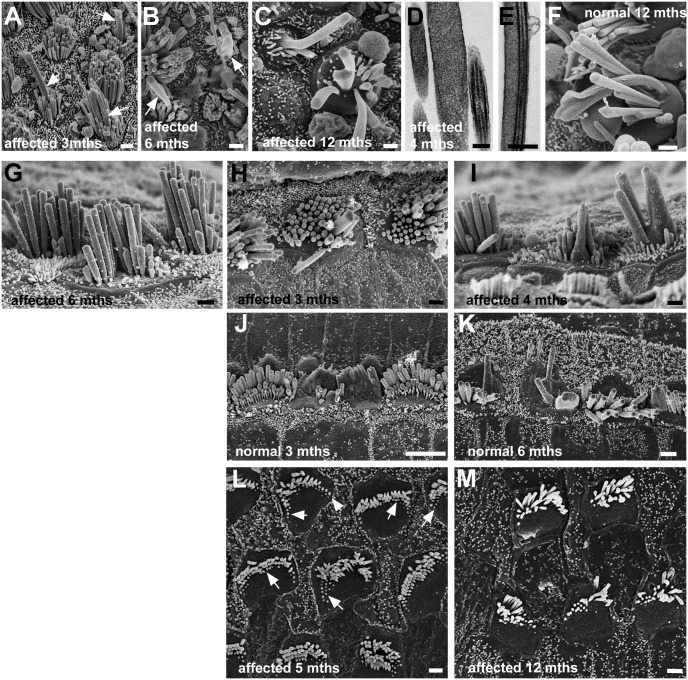
Fig 10. Ageing.
A-F: Utricles. A-E Affected animals: A: 3 months, B: 6 months, C: 1 year, D,E: 4 months. F: Normal animal at 1 year. A, B, C. Long, wide projections initially from centre of bundles (arrows in A,B), suggesting fusion of stereocilium with kinocilium, get longer and wider and incorporate more stereocilia (C) with age. Thin sections, show wide “stereocilia” (C) indicating fusion, and fusion of kinocilium and stereocilia (D). Similar fusion and elongation of stereocilia occurs with ageing in normal animals (F). G-K Cochlear inner hair cells. G-I: affected animals; J,K: normal animals. G. In the apical coil of an affected animal at 6 months of age, stereocilia are longer (ca. 4–5μm) than their counterparts in the younger affected animals. H, I: Fusion and elongation of stereocilia in scattered hair cells in affected animals. H: 3 months, upper basal coil; I: 4 months, middle coil. J, K: Similar fusion and elongation occurs in hair bundles of scattered IHC in normal animals. J, 3 months, littermate of animal in H, upper basal coil; K upper basal coil; 6 months. L,M. Cochlear outer hair cells in affected animal. L: Apical coil at 5 months. Hair bundles show stumps of stereocilia particularly at outer edges (arrows) suggesting retraction into the cell. M: Apical coil at 1 year. There are fewer stereocilia in bundles and continuing apparent retraction is evident. Scale bars: A, B, C 1μm; D 0.2μm; E 0.5μm; F-I 1μm; J 5μm; K 2μm; L,M 1μm.