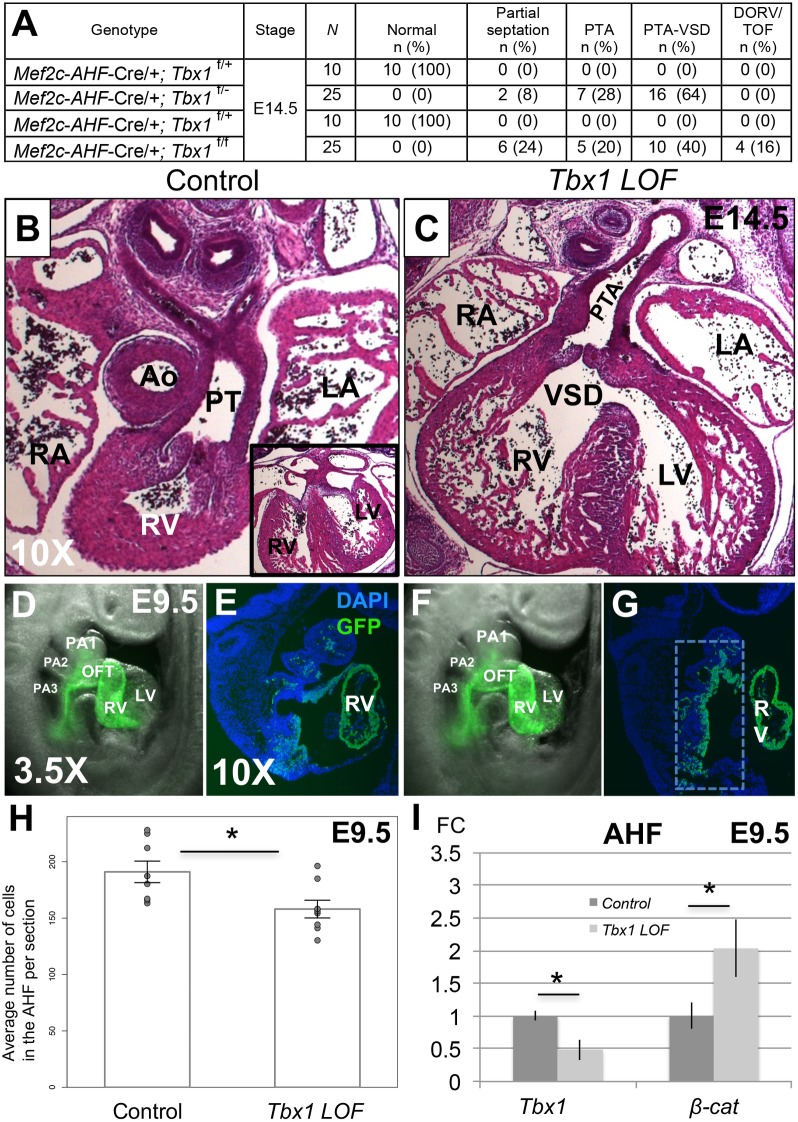
Fig 2. Congenital heart defects in Tbx1 LOF embryos.
(A) Heart phenotype analysis of Tbx1 LOF embryos at E14.5 generated from two different crosses. PTA-VSD refers to a PTA associated with a ventricular septal defect (VSD) while PTA refers to hearts that did not show a VSD. Partial septation in Tbx1 LOF embryos means a PTA with presence of a short septum at some level of the OFT and complete septation between the ventricles. N = total number of hearts observed per group. Significance between Tbx1 LOF and controls calculated by Fisher’s exact test (p < 0.001). Note that Mef2c-AHF-Cre;Tbx1flox/flox embryos had additional phenotypes (three with double outlet right ventricle, DORV and one with tetralogy of Fallot, TOF, as indicated); (B) H&E histological sections of the heart of a control embryo at E14.5, with a typical ventricular septum is shown in the inset on the lower right part of the image. (C) Tbx1 LOF embryo with a PTA-VSD. (D) Mef2c-AHF-Cre lineage tracing by using a GFP reporter allele in a control embryo at E9.5 and a representative sagittal section is shown in E. (F) Mef2c-AHF-Cre lineage tracing in a Tbx1 LOF embryo and a representative sagittal section of the embryo is shown in G. DAPI fluorescent stain to visualize nuclei and identify the tissue is shown in blue. (H) Mef2c-AHF-Cre lineage quantification from the area shown in the inset in G for control and Tbx1 LOF embryos. (I) Detection of Tbx1 and β-catenin by qRT-PCR in control and Tbx1 LOF embryos. Statistical significance of the difference in gene expression was estimated using two-tailed t-test, FC = fold change, p values < 0.05. Error bars = standard deviation (SD). Abbreviations: aorta (Ao), pulmonary trunk (PT), left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), left ventricle (LV), right ventricle (RV), pharyngeal arch (PA), outflow tract (OFT), 1, 2 and 3 indicate the first, second and third pharyngeal arches (PA), respectively.