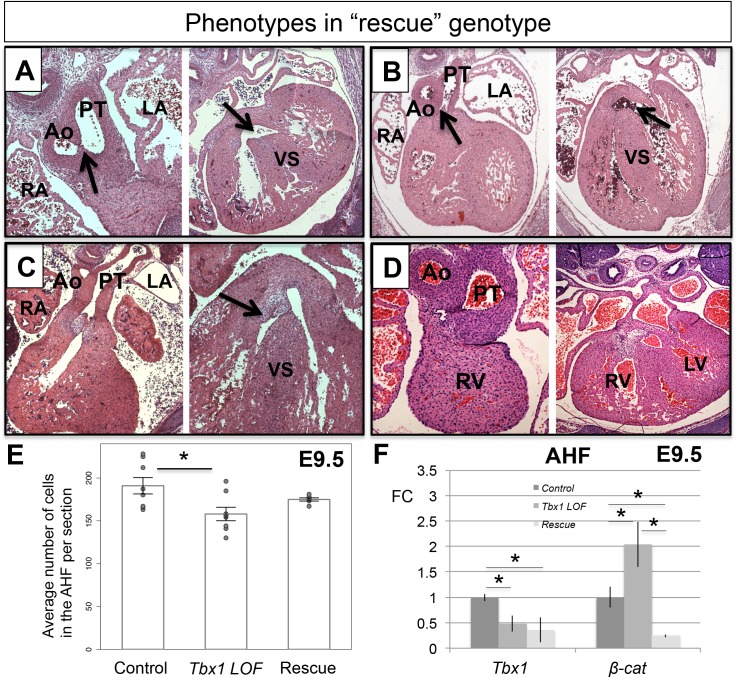
Fig 5. Histology analysis of representative embryos with the “rescue” genotype.
Transverse H&E histological sections of hearts from E14.5 significantly rescued embryos (Tbx1 LOF with loss of one allele of β-catenin in the Mef2c-AHF-Cre domain). (A) An embryonic heart with a thin septum formed that separates the Ao and the PT (top black arrow), and a small VSD compared to the usual PTA-VSD in Tbx1 LOF embryos (Fig 2C). (B) Example showing a DORV (middle black arrow), with a separate Ao and PT; normal ventricular septation is present. (C) Example of a heart showing a partially rescued septation between the Ao and PT (middle black arrow) and normal septation between the two ventricles (right black arrow). (D) Rescued septation between the Ao and PT. (E) Mef2c-AHF-Cre lineage quantification from the same area shown in Fig 2G for control, Tbx1 LOF and rescued embryos. (F) Detection of Tbx1 and β-catenin by qRT-PCR in control, Tbx1 LOF and rescued embryos. Statistical significance of the difference in gene expression was estimated using two-tailed t-test, FC = fold change, p values < 0.05. Error bars = standard deviation (SD). Abbreviations: RA = right atrium, RV = right ventricle, LA = left atrium, LV = left ventricle, Ao = Aorta, PT = pulmonary trunk, VS = ventricular septum, PTA = persistent truncus arteriosus, VSD = ventricular septal defect, DORV = double outlet right ventricle, OFT = outflow tract.