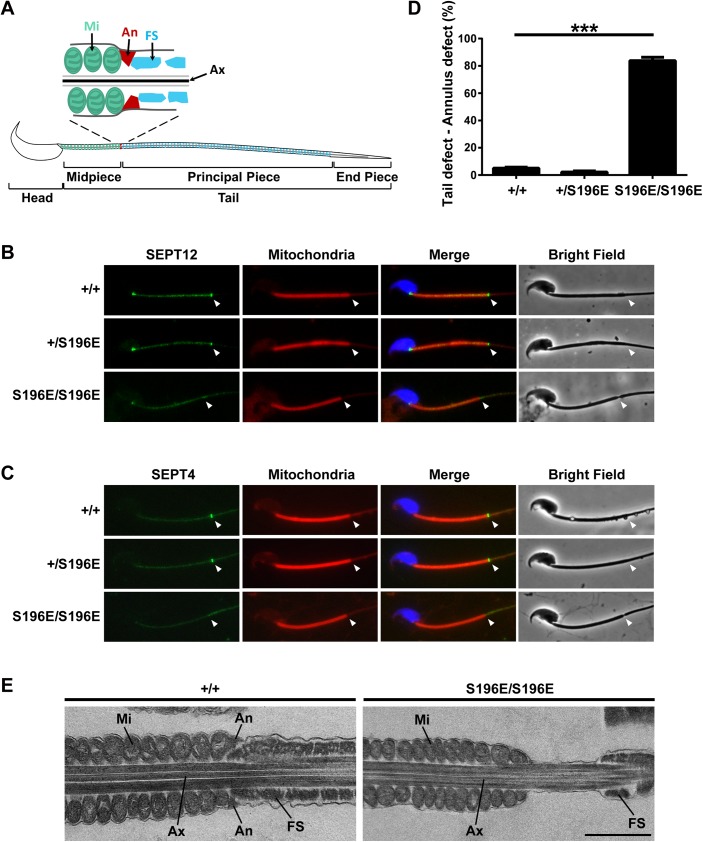
Fig 2. The annulus was absent in SEPT12S196E/S196E spermatozoa.
(A) Schematic representation of mouse spermatozoa. The annulus (An) is located between the mitochondria (Mi) in the midpiece and the fibrous sheath (FS) in the principal piece of the sperm tail. Ax, axoneme. (B, C) Immunofluorescence images of SEPT12 (B, green) or SEPT4 (C, green) from WT and SEPT12 KI spermatozoa. The middle piece was visualized through mitochondrial staining (Mito-Tracker, red). Nuclear staining (DAPI, blue) and bright-field images are also shown. Annular regions are indicated with arrowheads. (D) Quantitative representation of the sperm tail defect in the annular region from WT and SEPT12 KI mice (Each genotype, N = 5). The data are presented as the means ± SEM. ***P<0.001. (E) Electron microscopy analysis of WT and SEPT12 homozygous KI spermatozoa. In WT spermatozoa, the annulus (An) was observed between the mitochondria (Mi) and fibrous sheath (FS). In contrast, the annulus was completely lost in SEPT12 homozygous KI spermatozoa. The sperm were isolated form the epididymal cauda. Ax, axoneme. Scale bar: 1 μm.