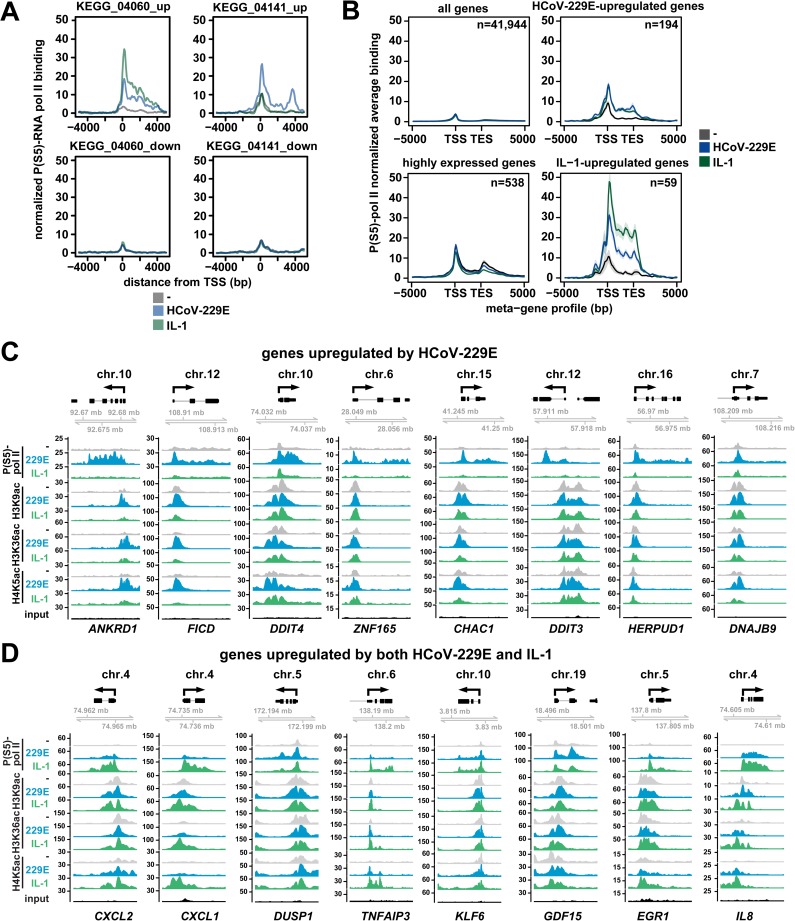
Fig 3. HCoV-229E replication is linked to specific binding patterns of active RNA polymerase II that correlate with mRNA expression and inducible acetylation of histone H4K5.
(A, B) HuH7 cells were infected with HCoV-229E for 24 h or were treated with IL-1 for 1 h or were left untreated. ChIP-seq experiments were performed using an antibody against the transcription-initiating serine 5-phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II (P(S5)-pol II). Mapped reads were centered at the transcriptional start sites (TSS) of up- or downregulated genes of KEGG clusters 04060 or 04141 as identified in Fig 2D and visualized as average profiles for each KEGG cluster. B) Meta-gene profiles of P(S5)-pol II recruitment according to mRNA expression levels for all genes, for highly expressed genes (log2(intensity) on microarrays >13) and for HCoV-229E- and IL-1-upregulated genes +/- 5 kb around gene bodies. Lines indicate means, shadows indicate confidence intervals (mean +/- 2 s.e.m.). Regulated genes were selected based on 4-fold cut-offs using microarray data from two (IL-1) or four (HCoV-229E) biological replicates as shown in Fig 2. (C, D) Browser views of P(S5)-pol II recruitment patterns and histone modifications of genes induced specifically by HCoV-229E (C) or by both IL-1 and HCoV-229E (D). Genes were selected on the basis of their mRNA induction as shown in Fig 2B and 2D. Y-axes show normalized read counts. See also S4 Fig.