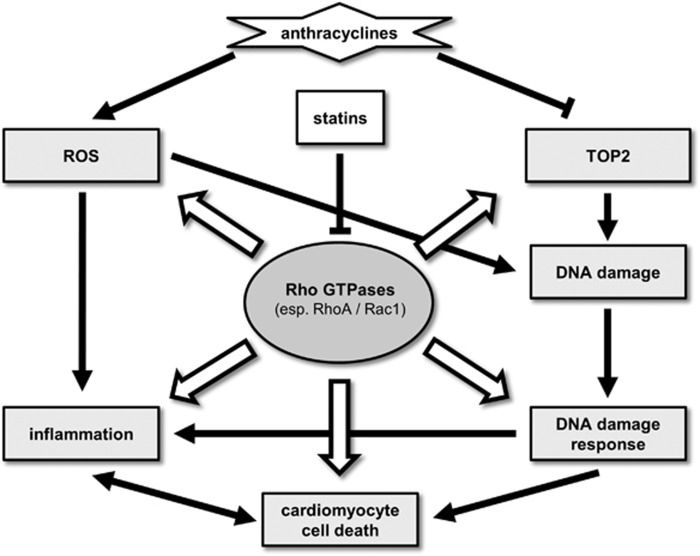
Figure 4.
Rho GTPases are involved in the regulation of main factors in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Anthracyclines induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) by redox cycling as well as Fenton's reaction. ROS induce oxidative DNA damage and are a driver of inflammation. In addition, anthracyclines inhibit type II topoisomerases (TOP2), causing highly cytotoxic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which forcefully trigger a pro-apoptotic DNA damage response and can ultimately result in cardiomyocyte cell death. Rho GTPases such as RhoA or Rac1 are known to play a role in the regulation of cell death and survival. Rac1 is described to regulate ROS production via the NADPH oxidase complex, RhoA and Rac1 participate in the regulation of inflammatory processes by (among others) altering NF-κB signaling after genotoxic insults. Oxidized guanine can act as GEF for nuclear Rac1, making this Rho GTPase a possible novel factor in the regulation of the DNA damage response. In addition, Rac1 is described to interact with type II topoisomerases