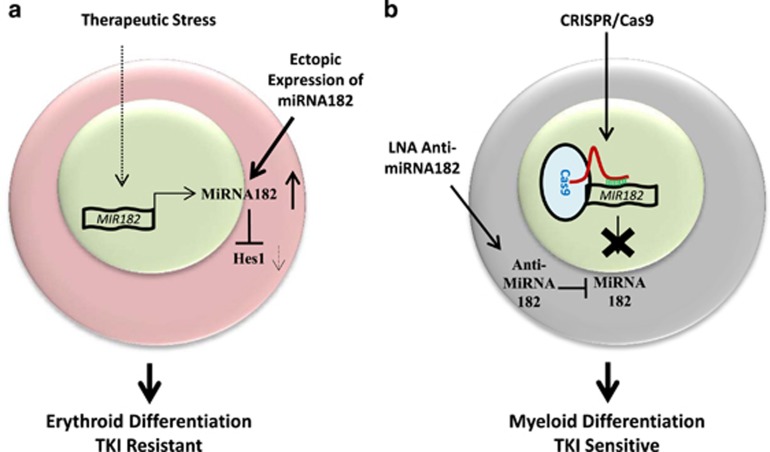
Figure 7.
MiRNA182-5p-mediated control over differentiation program contributes to TKI resistance of CML cells. (a) A cartoon diagram representing the mechanisms of miRNA182-mediated erythroid differentiation in K562 cells. The TK inhibitor induces the overexpression of miRNA182-5p that results in suppression of Hes1 expression. The cells acquire erythroid phenotype and become TKI resistant. Ectopically overexpressed miRNA182-5p leads to erythroid differentiation of K562 cells. The dotted arrows show correlation based on the expression. The solid arrows show direct interactions. (b) A cartoon diagram representing the myeloid differentiation in K562 cells mediated by the loss of miRNA182-5p expression. First, CRISPR system targeting MIR182 locus abrogates miRNA182-5p expression. This leads to myeloid differentiation of K562 cells. The transfection of anti-miRNA182-5p in K562 cells also induces a myeloid-biased phenotype and TKI sensitivity