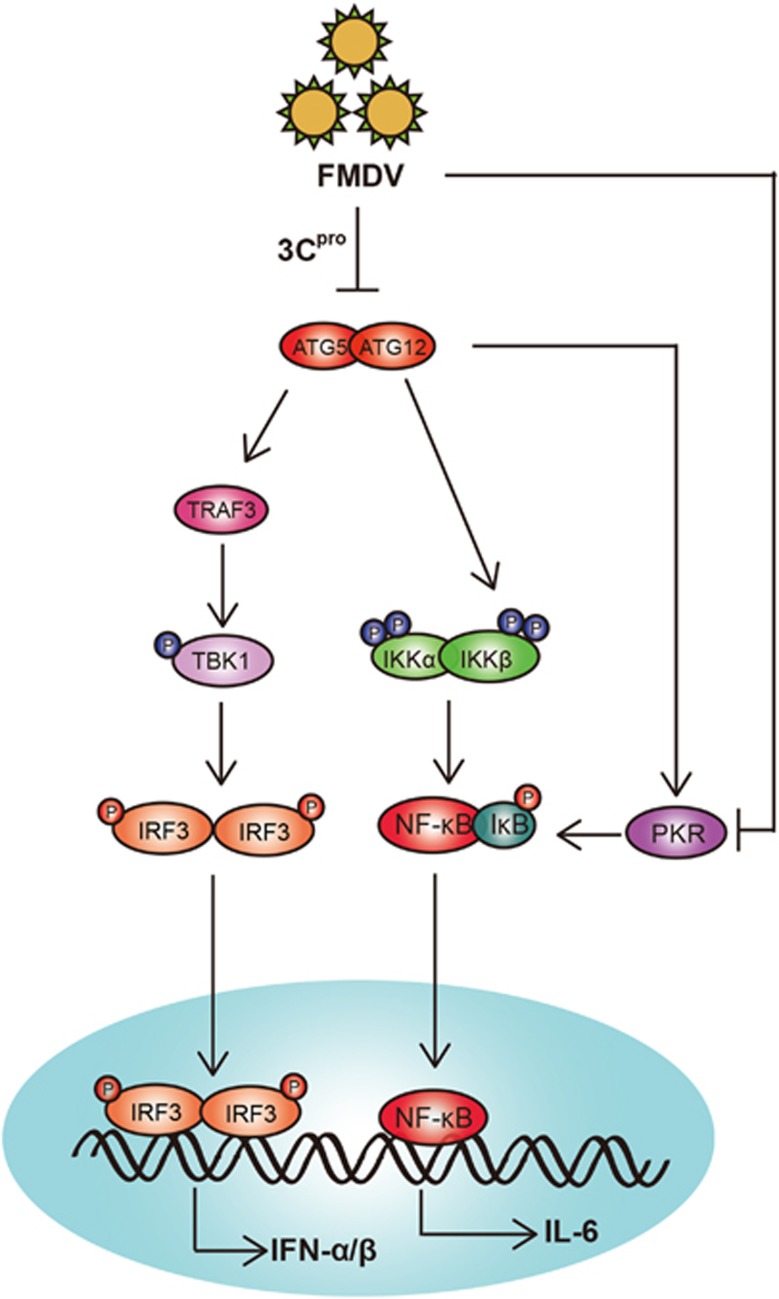
Figure 8.
Model of ATG5-ATG12 involvement in FMDV-induced type IIFN signal pathway. FMDV infection rapidly induces autophagy. Subsequently, the autophagy is probably suppressed via degradation of ATG5 and ATG12 via FMDV 3Cpro. Replenishment of ATG5-ATG12 conjugate promotes the phosphorylation of IKKα/β, phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα, subsequently promoting the nuclear translocation of p65. Meanwhile, ATG5-ATG12 increases the IRF3 activity through stabilizing TRAF3 and increasing the phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3. Moreover, ATG5-ATG12 also can block the FMDV-trigged PKR reduction, resulting in increased p-IkB and the subsequent activation of NF-κB. Then the activation of NF-κB and IRF upregulates the transcription of kB-dependent genes and type I IFN