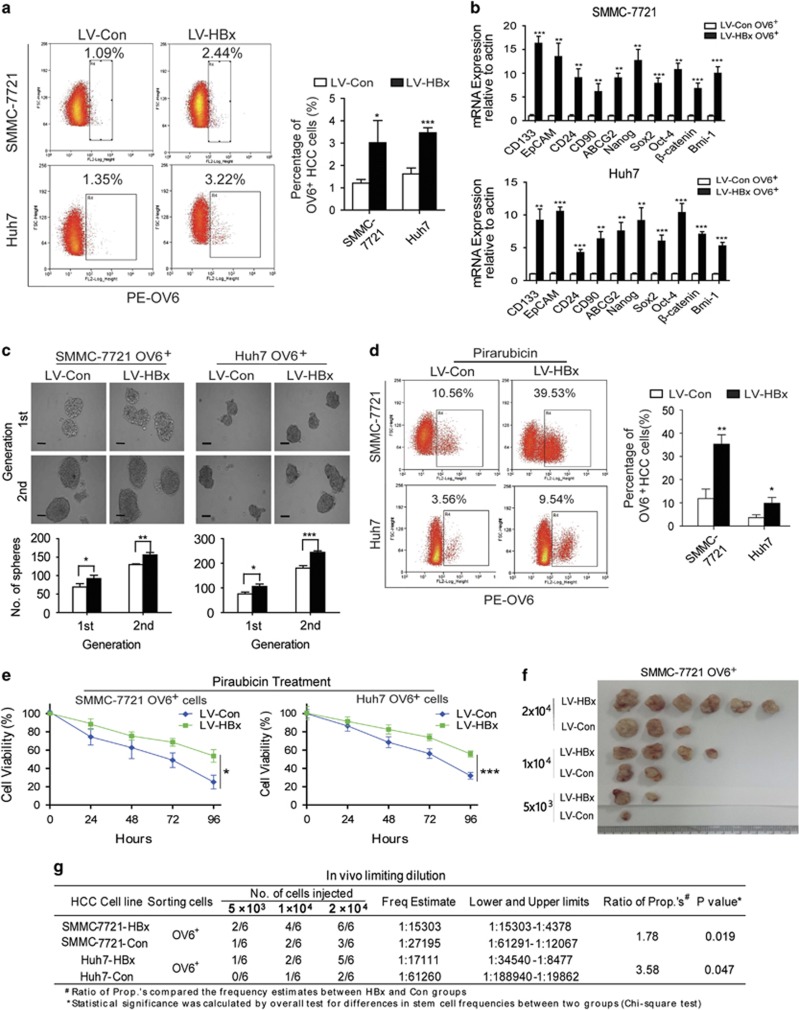
Figure 2.
HBx enhances the stem cell-like properties and tumorigenic potential of OV6+ liver CSCs. (a) The percentage of OV6+ cells among the SMMC-7721 and Huh7 cells stably expressing either LV-HBx or LV-Con was measured via flow cytometry and presented as a dot plot analysis. Representative images are shown in the left panel. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and all data are shown as the mean±S.D. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001. (b) The mRNA expression levels of multiple stemness-related genes in magnetically sorted LV-HBx OV6+ or LV-Con OV6+ cells from SMMC-7721 and Huh7 cultures were evaluated by qRT-PCR. The fold change was determined using the delta-delta Ct method. Quantified mRNA levels were normalized to β-actin and presented relative to the controls. The data are presented as the mean±S.D. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (c) Representative images of primary and secondary passages of HCC spheres derived from magnetically sorted HCC-LV-HBx OV6+ and LV-Con OV6+ cells are shown (Scale bar=50 μm; upper panel), and the number of tumor spheroids was counted (lower panel). Experiments were performed in triplicate, and results display the mean±S.D. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (d) HCC cells infected with either LV-HBx or LV-Con were treated with 5 μM pirarubicin for 4 days, and the percentage of OV6+ cells were detected via flow cytometry. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. (e) OV6+ HCC cells were treated with 5 μM pirarubicin, and cell viability was measured by using the CCK-8 assay at the indicated time points. **P<0.05 and ***P<0.001. (f and g) Male NOD/SCID mice were subcutaneously injected with the indicated number of OV6+ HCC cells infected with either LV-HBx or LV-Con, and the tumor incidence in the mouse xenografts was evaluated. Representative subcutaneous xenograft tumors from mice injected with a gradient series of lentivirus-infected OV6+ cells after 6 weeks of transplantation are shown. The percentage of CSCs present was evaluated 6 weeks after injection by a limiting dilution assay