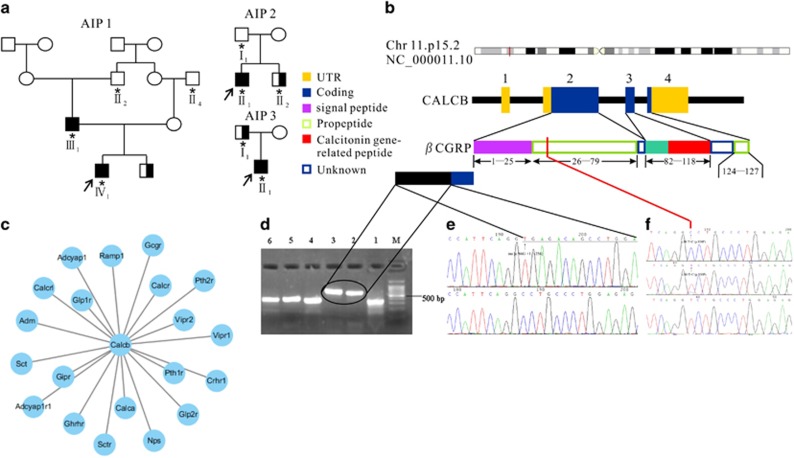
Figure 1.
Identification of CALCB mutations in type 1 AIP. (a) The pedigrees of the three families affected by type 1 AIP (AIP1, AIP2, and AIP3), AIP patients (▪), Type II Diabetes Mellitus patients (▪) and their family normal members (○□), DNA collected (*), Proband (↗). (b) βCGRP protein domain structure. The CALCB gene contains five exons that encode several domains in the βCGRP protein, including two propeptide domains, two unknown domains and one signal peptide domain. (c) Protein–protein interaction network of CALCB. (d) RT-PCR analysis of CALCB mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. M: Marker, Lane 1: normal control, lane 2 and lane 3: INS [c.86 G +1:+256], lane 4–6: normal control. (e) INS [c.86 G +1:+256] mutation and the resultant mutant mRNA retains the first intron which were validated by Sanger sequencing. (f) c.88T>C in exon 2 (homozygous: top; heterozygous: middle; normal: bottom). The location of the mutation is indicated by the vertical arrows