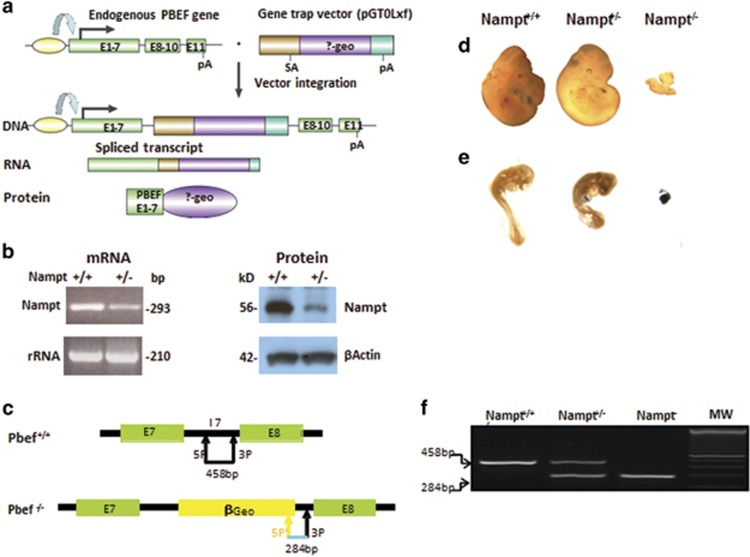
Figure 1.
Homozygous Nampt gene knockout mice are embryonically lethal. (a) The schematics of gene-trap strategy to create Nampt knockout mice. Gene-trap cassette were inserted in Nampt gene intron-7 and the transcription of the ‘trapped' Nampt gene results in a truncated mRNA that will translate into a Nampt exon 1–7 and β-geo fusion protein. (b) Phenotypic verification of Nampt gene-trapped embryonic stem (ES) cell line. Phenotypic verifications of an ES cell line (RRR084) with Nampt gene interruption (Nampt+/−) were carried out by RT-PCR for Nampt mRNA and western blotting for Nampt protein expression. Nampt+/+ represents wild-type ES cell line without a gene-trap vector insertion. (c) Genotyping strategy. Mouse yolk sac or tail DNA was used for genotyping by PCR. The locations of Nampt gene intron-7 and β-Geo specific primers used for genotyping and predicted size of the PCR products are shown. (d) Representative mouse embryos at 11.5 d.p.c. Timed pregnancies and embryo collection were carried out as described in the 'Materials and Methods' section. Mouse embryo images from representative Nampt+/+ , Nampt+/−, and Nampt−/− mice at 11.5 d.p.c. are displayed. (e) Representative mouse embryos at 8.5 d.p.c. Timed pregnancies and embryo collection were carried out as described in the 'Materials and Methods' section. Mouse embryo images from representative Nampt+/+, Nampt+/−, and Nampt−/− mice at 8.5 d.p.c. after β-Gal staining are displayed. (f) Representative genotyping images. Mouse genotyping was done using PCR amplification of genomic DNA isolated from mouse embryonic tissue or yolk sac with either primer pairs 5P and 3P or 5P' and 3P as depicted in c. The PCR products were subjected to 2% agarose electrophoresis and stained by ethidium bromide