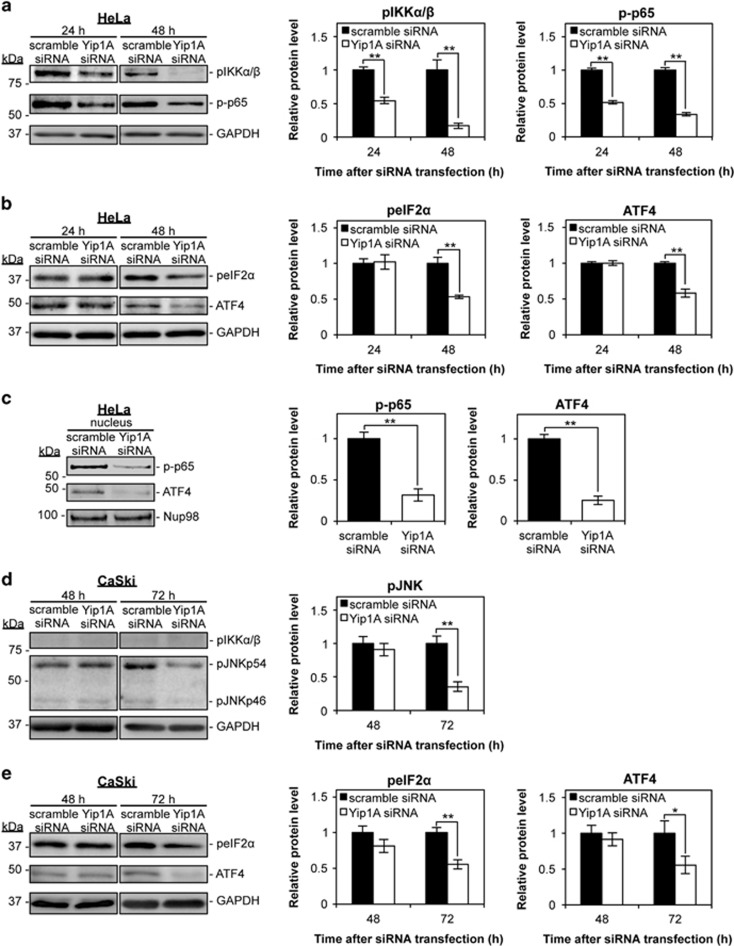
Figure 3.
Depletion of Yip1A impairs signaling downstream of the IRE1 and PERK pathways. (a) HeLa cells were treated with control scramble siRNA or Yip1A siRNA and the cell lysates were prepared at the indicated time points. Western blotting shows the relative levels of phosphorylated IKKα/β (pIKKα/β) and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 (p-p65) protein in control and Yip1A-knockdown cells at 24 h and 48 h after siRNA transfection. GAPDH was used for normalization. Data are means±S.D. from three independent experiments; **P<0.01. (b) Western blotting shows the relative levels of phosphorylated eIF2α (peIF2α) and ATF4 protein in control and Yip1A-knockdown cells at 24 h and 48 h after siRNA transfection. GAPDH was used for normalization. Data are means±S.D. from three independent experiments; **P<0.01. (c) Western blotting shows relative levels of p-p65 and ATF4 protein in the nuclear fraction of control and Yip1A-knockdown HeLa cells at 48 h after siRNA transfection. Nup98 was used as a control for loading of the nuclear fraction. Data are means±S.D. from three independent experiments; **P<0.01. (d) CaSki cells were treated with control scramble siRNA or Yip1A siRNA and the cell lysates were prepared at the indicated time points. Western blotting shows the relative levels of pIKKα/β and phosphorylated JNK (pJNKp46 and pJNKp54) protein in control and Yip1A-knockdown cells at 48 h and 72 h after siRNA transfection. GAPDH was used for normalization. Data are means±S.D. from three independent experiments; **P<0.01. (e) Western blotting shows the relative levels of peIF2α and ATF4 protein in control and Yip1A-knockdown cells at 48 h and 72 h after siRNA transfection. GAPDH was used for normalization. Data are means±S.D. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01