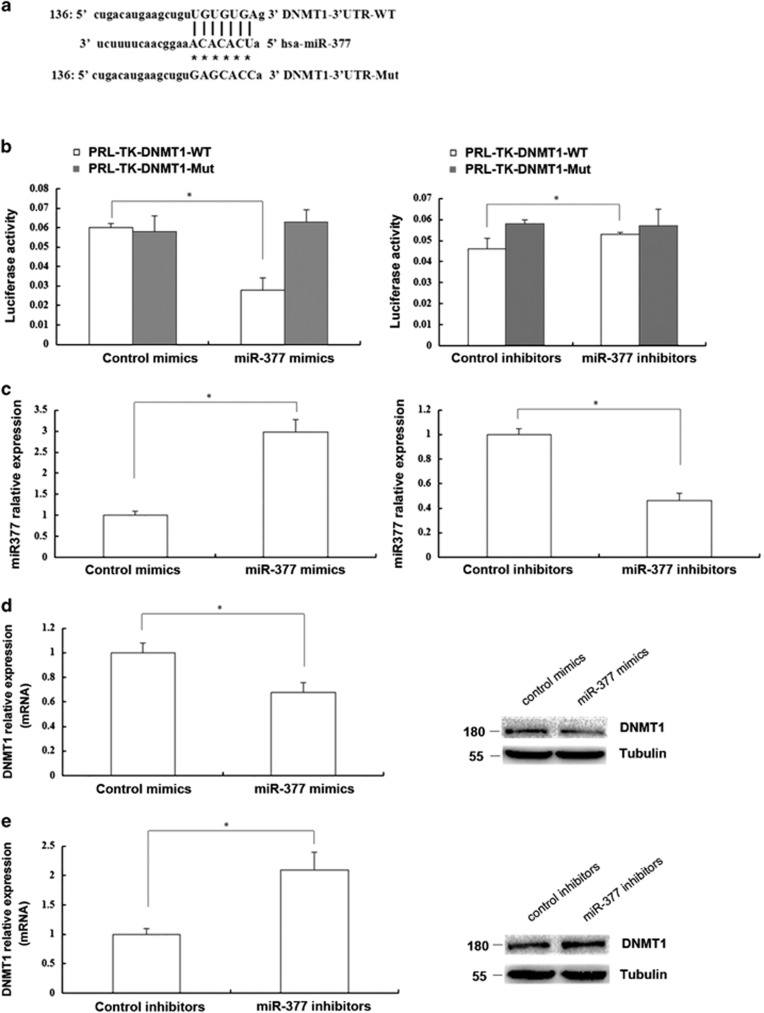
Figure 2.
miR-377 could regulate DNMT1 expression by directly targeting DNMT1 in HSFs. (a) Though bioinformatics prediction, the sequence of the miR-377 binding site in the 3′-UTR of DNMT1 was shown at the upper site. Mutated residues were shown at the lower site. (b) Luciferase activity change of the wild-type 3′-UTR reporters and the mutant 3′-UTR reporters in 293T cells treated with control mimics or miR-377 mimics (left) and 293T cells treated with control inhibitors or miR-377 inhibitors (right) was shown, respectively (Data represented as the mean±S.E.M. n=3, *P<0.05, respectively). (c) miR-377 level in young HSFs (PD<10) treated with control mimics or miR-377 mimics (left) and in passage-aged HSFs (PD>50) treated with control inhibitors or miR-377 inhibitors (right) was respectively detected by RT-qPCR (Data represented as the mean±S.E.M. n=3, *P<0.05, respectively). (d) DNMT1 mRNA and protein expression in the young HSFs (PD<10) treated with control mimics or miR-377 mimics was detected by RT-qPCR and western blot, respectively (Data represent the mean±S.E.M. n=3, *P<0.05). (e) DNMT1 mRNA and protein expression in the passage-aged HSFs (PD>50) treated with control inhibitors or miR-377 inhibitors was detected by RT-qPCR and western blot, respectively (Data represent the mean±S.E.M. n=3, *P<0.05)