Figure 3. Effects of DAC-induced Bin1 de-methylation on ESCC cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
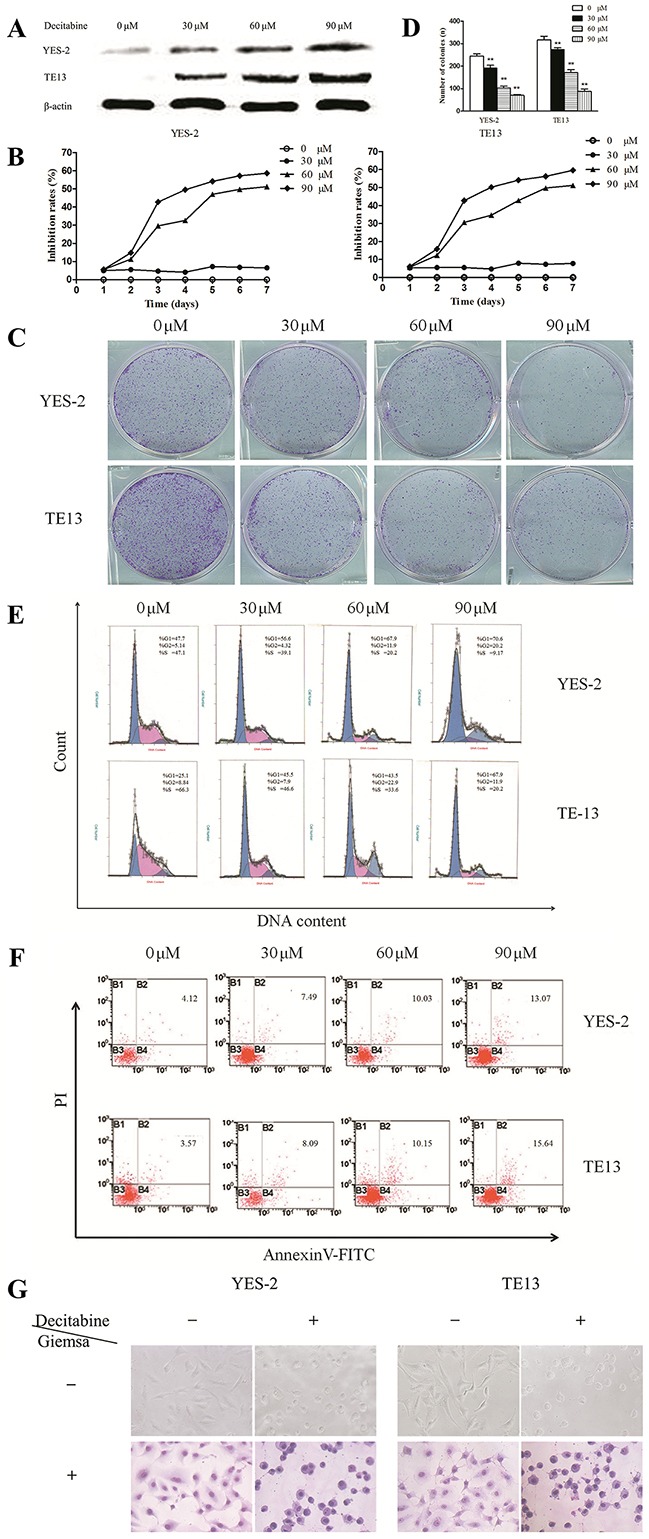
A. Protein expression of Bin1 in YES-2 and TE13 cells restored at different concentrations (0, 30, 60, and 90 μM) of DAC detected by western blot. B. Effect of DAC at different concentrations (0, 30, 60, and 90 μM) on the proliferation inhibition rate for 7 days investigated using MTT. The rate of proliferation was calculated (n = 3). C. and D. Significant inhibition of cell colony formation was observed upon treatment with DAC (0, 30, 60, and 90 μM) for 10 days, the number of colonies was counted and plotted on the histogram. E. Effect of DAC at different concentrations (0, 30, 60, and 90 μM) on the cell cycle was investigated using FCM. Representative histograms of PI stained cells. The cell cycle of the two cells arrested in the G0/G1 phase was calculated. F. The effect of DAC on the apoptotic rate of YES-2 and TE13 cells was detected through FCM analysis, and YES-2 and TE13 cells were treated at different concentrations (0, 30, 60, and 90 μM) of DAC. After 72 h, the cells were collected for apoptosis analysis. The percentages of annexin V- or propidium iodide-positive cells were detected using FCM. G. The effects of DAC on the cell morphology of YES-2 and TE13 were observed using an optical microscope with or without Giemsa staining. ** P < 0.01
