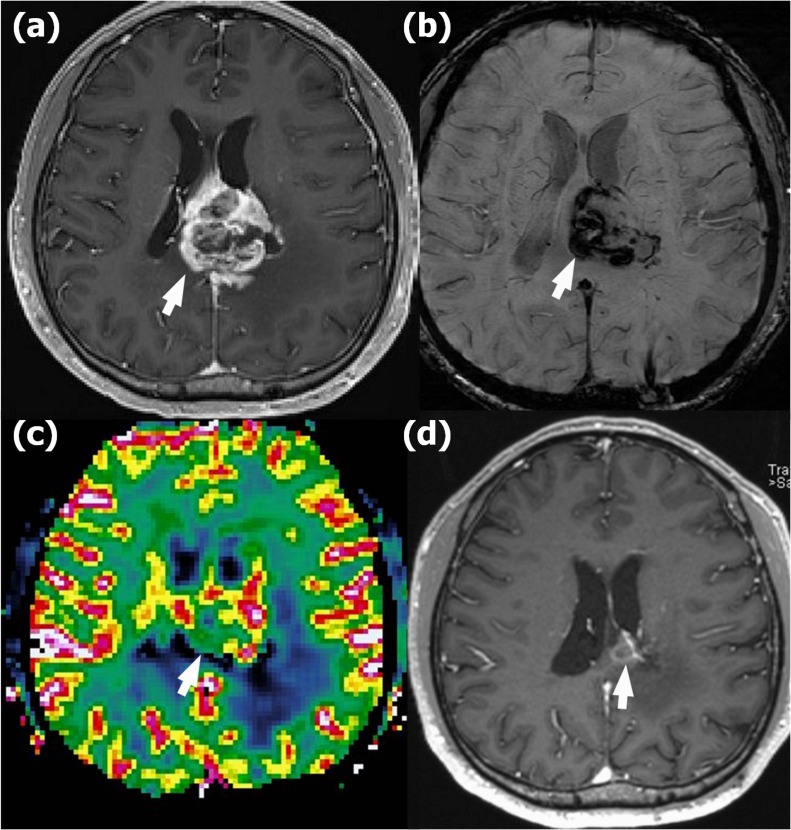
Figure 5. Radionecrosis in a 41-year-old man with glioblastoma in the left mid corpus callosum who underwent gross total resection and concomitant chemoradiotherapy (CCRT).
a. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (CET1) magnetic resonance (MR) image obtained 18 months after CCRT completion shows newly appearing enhancing lesions in the left mid corpus callosum (arrow). b. Susceptibility-weighted imaging demonstrates significant dark areas in the corresponding enhancing lesions (arrow); the proportion of dark signal intensity (proSWMRI) was 40.5 %. c. The normalized relative cerebral blood volume map (nCBV) from dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted imaging shows increased blood flow in the corresponding enhancing area (arrow) (calculated 90th percentile points in the cumulative nCBV histogram (nCBV90) = 2.84). d. Follow-up CET1 MR image obtained 36 months after the first appearance of the enhancing lesion shows an interval decrease in the extent of the enhancing lesion (arrow), suggesting radionecrosis.