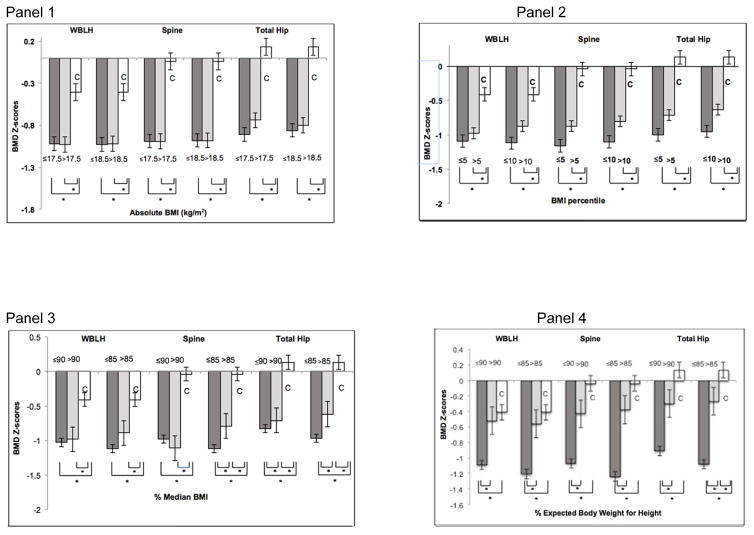
Figure 1.
Bone mineral density (BMD) Z-scores of whole body less head (WBLH), lumbar spine (spine), and total hip skeletal sites across tested low-weight parameters in participants with Anorexia Nervosa (AN) and healthy controls (C).
Panel 1: BMD Z-scores of AN participants based on body mass index (BMI) cut-offs 17.5 and 18.5 (gray bars), and controls (white bars). BMD Z-scores at all sites are lower in both groups of AN participants compared with controls. However, within participants with AN, having a BMI less than or greater than 17.5 or 18.5 does not predict lower BMD Z-scores. *p<0.05.
Panel 2: BMD Z-scores of AN participants based on BMI percentile cut-offs; 5th and 10th (gray bars) and controls (white bars). BMD Z-scores at all sites are lower in both groups of AN participants compared with controls. However, within participants with AN, those with a BMI percentile less than the 10th percentile have significantly lower total hip BMD Z-scores than those with a BMI percentile above the 10th percentile. *p<0.05.
Panel 3: BMD Z-scores of AN participants based on median BMI (mBMI) cut-offs 85% and 90% (gray bars) and controls (white bars). BMD Z-scores at all sites are lower in both groups of AN participants compared with controls. Within AN participants, those with mBMI >85% have higher total hip and lumbar spine BMD Z-scores than those with mBMI ≤85%, and AN participants with mBMI >90% have higher total hip BMD-Z scores than those with mBMI ≤90%. *p<0.05.
Panel 4: BMD Z-scores of anorexia nervosa (AN) participants based on % EBW-Ht cut-offs 85% and 90% (gray bars) and controls (white bars). BMD Z-scores at all sites are lower in AN participants with % EBW-Ht ≤85% and ≤90% compared with controls. At all sites, BMD Z-scores are lower in AN participants with % EBW-Ht ≤85% and ≤90% than AN participants with >85% and >90% respectively. Patients with %EBW-Ht ≤85% have significantly lower total hip BMD-Z scores compared with controls. * p<0.05.