Fig. 2. Simplified representation of major signal transduction pathways regulating coordinate control of microglia chemotaxis.
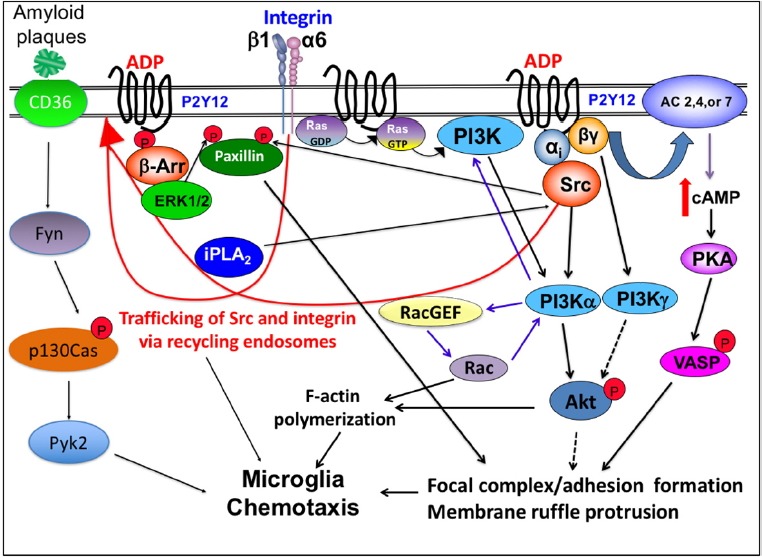
Chemoattractant (ADP or ATP) triggers signaling by activating its specific Gi/o-coupled receptor, P2Y12, which leads to the elevation of PI(3,4,5)P3 by the activation of PI3Kα via Gαi and PI3Kγ via Gβγ, leading to the activation of Akt. Ras is activated at the leading edge and also important for the activation of the PI3K pathway. Gβγ released from Gαi also can elevate intracellular cAMP by the activation of AC, causing VASP phosphorylation by PKA. Activation of Src via Gαi causes phosphorylation of paxillin at Tyr31, which is essential for focal adhesion assembly. ADP stimulation of P2Y12R recruits β-arrestin which recruits and activates ERK1/2. ERK1/2 phosphorylates Ser83 of paxillin that is required for adhesion disassembly. Activation of P2Y12R increases iPLA2 activity which is required for the vesicular recycling of integrin and Src.
