Figure 1.
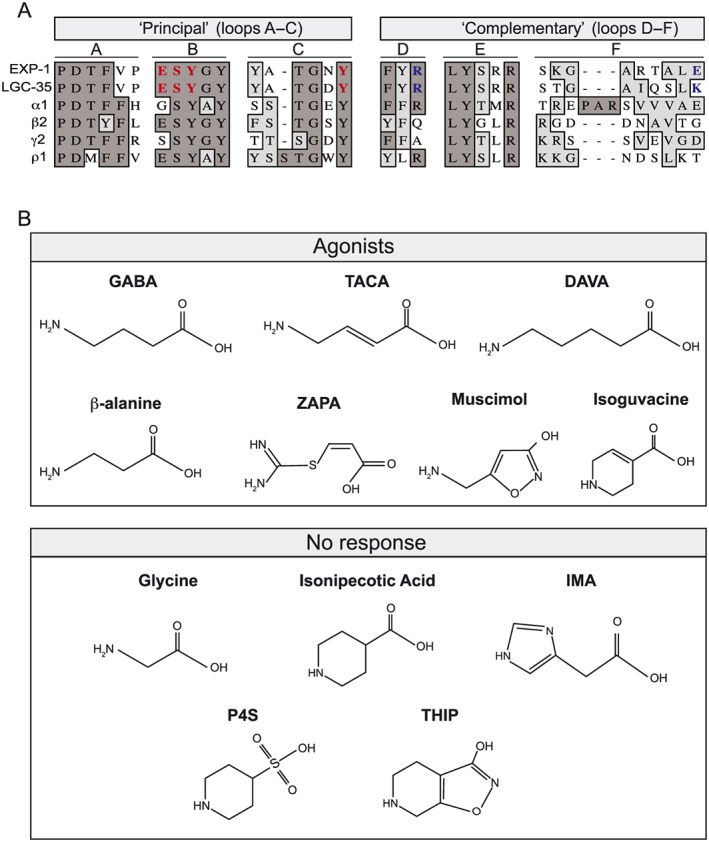
The orthosteric binding sites of EXP‐1 and LGC‐35 are highly conserved. (A) Sequence alignment of amino acid motifs (loops A–F) that comprise the orthosteric GABA binding site. GABA binding occurs at the subunit interface of two adjacent subunits termed the ‘principal’ and ‘complementary’ subunit. The orthosteric binding site is formed from three loops on the ‘principal’ subunit (loops A–C) and three β‐sheets on the ‘complementary’ subunit (loops D–F). Residue identity is indicated in dark grey and similarity in light grey highlights. Residues involved in ligand binding in this study are bold‐highlighted red (principal), and blue (complementary). Aligned protein sequences, C. elegans EXP‐1 and LGC‐35, human GABAA receptor subunits (α1, β2 and γ2) and human GABAA‐ρ subunit (ρ1). (B) Structures of known agonists at GABAA receptors that were assayed for agonist activity at EXP‐1 and LGC‐35. Compounds that directly activated are categorized as agonists, and those that elicited no activity are categorized as no response.
