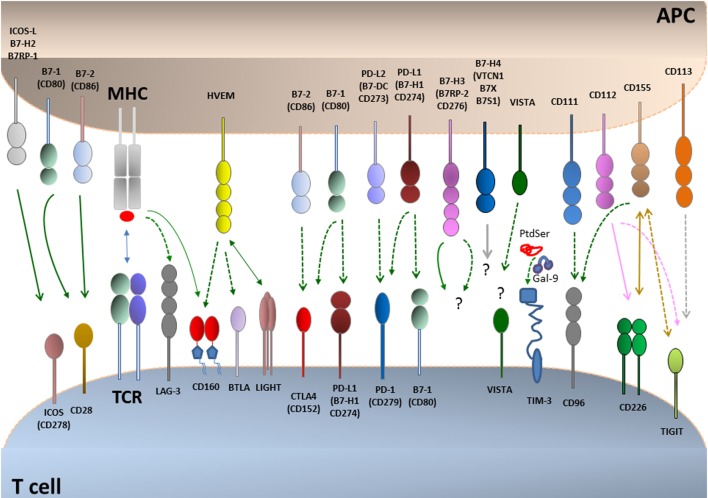
Figure 1.
Coinhibitory pathways. T cell activation is initiated by recognition of antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to the T cell receptor (TCR)–CD3 complex in the presence of CD28 costimulation. CD28 is the prototype costimulatory receptor and interacts with CD80 and CD86. Many coinhibitory pathways are upregulated upon T cell activation and can attenuate TCR and costimulatory signals. Coinhibitory pathways in the B7–CD28 family control responses of naive, effector, regulatory, memory, and exhausted T cells. Ligands for coinhibitory receptors are expressed on APCs, non-hematopoietic cells, tumors, and some of them also on T cells. The receptors for B7-H3 and B7-H4 and their effects remain unclear. Binding ligands for VISTA have not been identified. Continuous lines indicate interactions mediating stimulatory effects, and dotted lines indicate interactions mediating inhibitory effects.