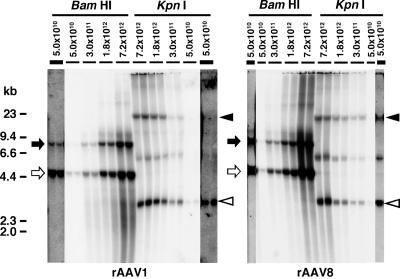
FIG. 3.
Southern blot analysis of rAAV vector genomes in liver transduced with AAV1- or AAV8-EF1α-nlslacZ at various doses. The left and right panels show the results obtained with AAV1-EF1α-nlslacZ- and AAV8-EF1α-nlslacZ-injected mice. Total genomic DNA was extracted from the livers harvested 6 weeks postinjection and separated on 0.8% agarose gels following BamHI or KpnI digestion. BamHI cleaves the vector genome only once at nucleotide position 1362, while KpnI does not cut the 4,828-base genome. The vector genomes were detected with a 2.1-kb lacZ probe (nucleotide positions 1518 to 3639). Each lane represents an individual mouse. Injected vector doses (vg per mouse) are indicated above each lane. For the results obtained from the mice injected with 5.0 × 1010 vg/mouse, strips from overexposed blots are also shown to demonstrate the presence or absence of concatemers. They are indicated with thicker lines above the lanes. Open and solid arrows indicate head-to-tail and tail-to-tail molecules, respectively. Open and solid arrowheads indicate supercoiled double-stranded circular monomer vector genomes and concatemers, respectively. Head-to-tail molecules include both circular monomer genomes and concatemers, while tail-to-tail molecules represent concatemers exclusively. Therefore, the intensity of tail-to-tail molecules well correlates with the abundance of concatemers.