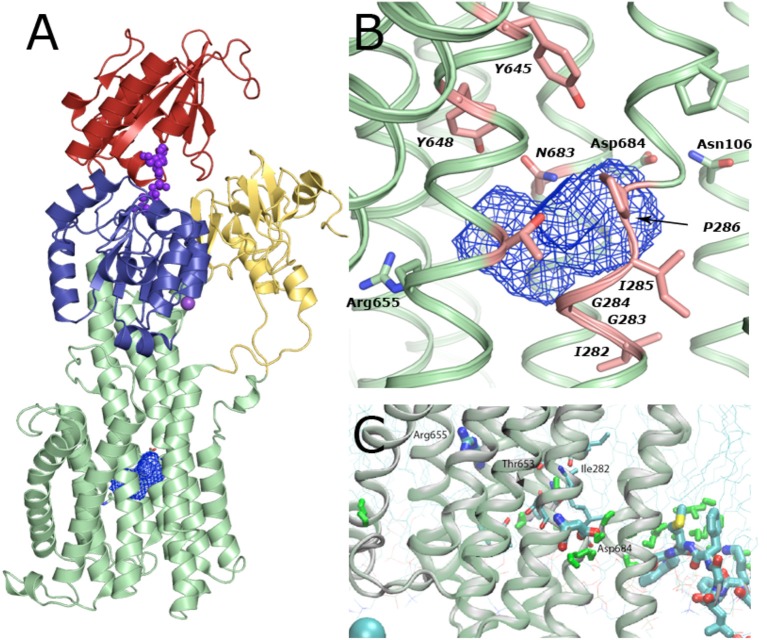
Figure 9.
Solvent cavity in the TM domain of AHA2. (A) Overview on the cavity location within the TM domain. The cavity likely encloses 8–10 bound water molecules in this conformation of the pump. (B) Zoom-in of the cavity viewed in the plane of the membrane. The cavity is formed by backbone atoms of Ile282, Gly283, and Ile285 along with Gly 284, Pro286 and side chains of conserved Tyr645, Tyr648, Tyr653, and Arg655 of TM5 and Asn683 of TM6. (C) Molecular Dynamics simulations indicate that a continuous string of water molecules (shown in green) can reach from the cytoplasm to the Asp684 residue, the proposed proton binding site, i.e., an open proton translocation pathway, which must close later in the functional cycle, most likely along with E1P formation. Two stable water molecules reached almost half way through the membrane into the TM domain where they can interact with Ile282, Thr653 and backbone oxygen of Ala649, and Cys247, next to the central solvent cavity.