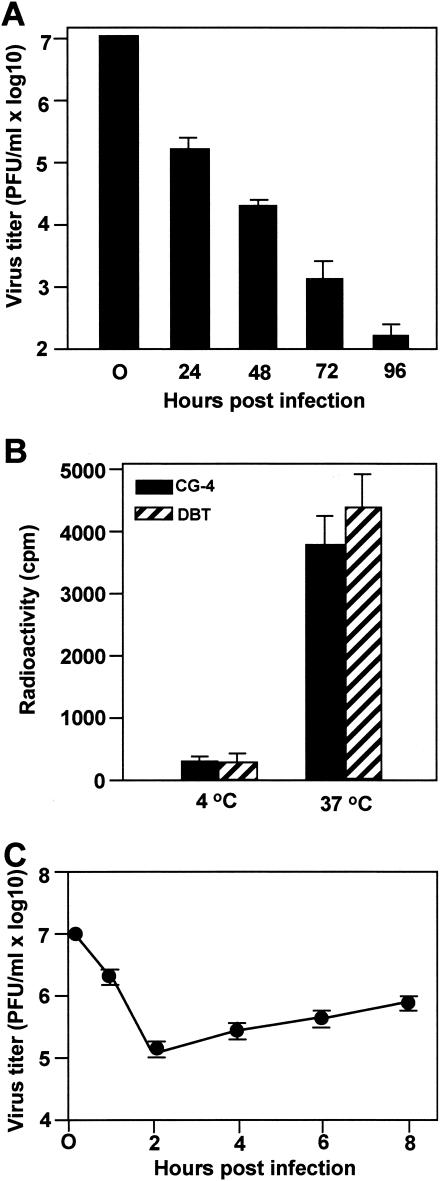
FIG. 1.
Internalization and replication of MHV in progenitor rat oligodendrocyte CG-4 cells. (A) CG-4 progenitor cells were grown in condition medium. Approximately 106 cells were infected with MHV strain JHM at an MOI of 10. At each time point p.i. as indicated, virus titers recovered from the culture were determined by plaque assay in DBT cells. The results are expressed as the mean PFU per milliliter for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations of the means. The virus titer at 0 h p.i. denotes the virus titer for the inoculum. (B) MHV strain JHM was grown in DBT cells and thevirus genomic RNAs were labeled with [3H]uridine as described in Materials and Methods. Radiolabeled viruses were then purified by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation and were used for infection of CG-4 cells. Infection of DBT cells permissive for MHV infection was used as a positive control. Virus attachment was carried out at 4°C for 1 h. After extensive washing of unbound viruses, one set of the cell cultures was moved to 37°C for an additional hour to allow internalization. The other set of cultures remained at 4°C for an additional hour. At the end of the second hour, bound but uninternalized viruses were removed by treatment with protease K. Cells were then lysed, and intracellular radioactivities were determined in a liquid scintillation counter. The results are expressed as the mean counts per minute (cpm) for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means. (C) One step-growth curve in progenitor CG-4 cells. The results are expressed as the mean PFU per milliliter for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means.