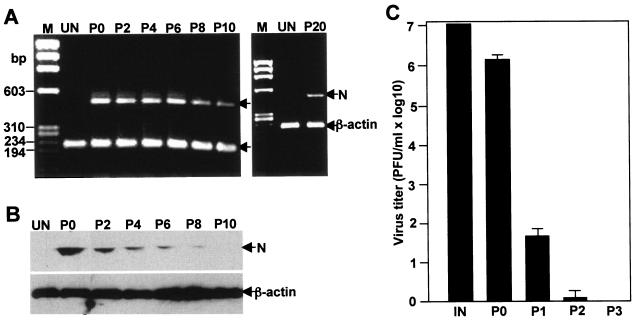
FIG. 6.
Overexpression of cellular oncogene Bcl-xL in CG-4 cells converts acute infection to persistent, nonproductive infection. CG-4 cells stably expressing Bcl-xL (CG-4/Bcl-xL) were either mock infected (UN) or infected with MHV at an MOI of 10. Cells that were initially infected with the virus are designated passage 0 (P0). Cells were then passaged every 3 days. The resultant passages are termed P1, P2, and so forth. Cells from each passage were analyzed for the presence of the viral N gene by RT-PCR (A), viral N protein by Western blotting (B), and infectious virus by plaque assay (C). (A) RT-PCR detection of viral N gene. After the extraction of total intracellular RNAs with the TRIzol reagent, cDNAs were synthesized with the random hexamer primer by RT. The N gene and the control β-actin gene were amplified in the same PCR with gene-specific primer pairs as described in Materials and Methods. RT-PCR products were analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Molecular size markers (M) in base pairs (bp) are shown on the left. The upper and lower bands in both panels are the N gene and β-actin gene, respectively, as indicated by arrows. (B) Western blot detection of viral N protein. Cellular proteins were extracted with the lysis buffer, separated by PAGE (10% gel), transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and detected with antibodies specific to MHV N protein, and β-actin as described in Materials and Methods. Arrows on the right indicate the specific protein bands. (C) Virus recovery from various cell passages. IN, input virus titer for primary infection. The results are expressed as the mean PFU per ml for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means.