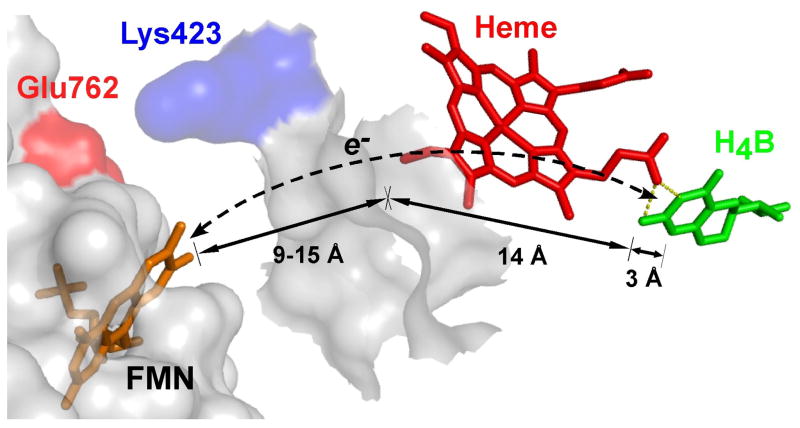
Fig. 3. Proposed through-heme pathway for the reduction of H4B radical in NOS.
The cartoon shows a portion of the FMN domain (semi-transparent white with an orange-bound FMN) docked onto a portion of the NOSoxy domain (semi-transparent white). The bound heme (red) in NOSoxy has an edge positioned near the proposed docking site for the FMN domain, and docking is possibly facilitated by electrostatic interaction of surface residues Glu762 and Lys423. The bound H4B (green) in NOSoxy is at least 17 Å away from the surface. A through-heme electron transfer pathway from FMN to H4B (dashed line) is indicated, along with the relevant distances marked by arrows. Adapted from Ref. [15].