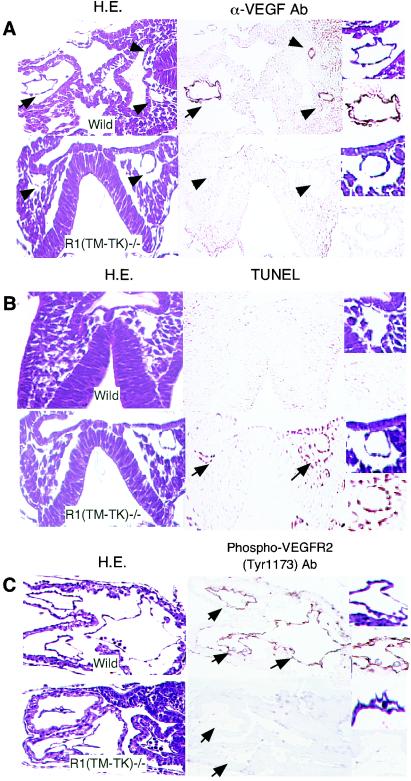
FIG. 3.
Reduced membrane-targeted VEGF in VEGFR1(TM-TK)−/− mice. (A) Transverse sections of wild-type and (TM-TK)−/− embryos at E8.0 stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H.E.; left panels) or an anti-mouse VEGF antibody (right panels). Arrows and arrowheads point to endothelial cells of the primitive heart and dorsal aorta, respectively. (B) Apoptosis of endothelial cells in the dorsal aorta (arrows) of a VEGFR1(TM-TK)−/− embryo at E8.0, as evidenced by TUNEL staining (right panels). (C) Phosphorylated VEGFR2 on endothelial cells was immunohistochemically detected by use of an antibody against phosphorylated Y1173 on VEGFR2, which is the major VEGF-dependent autophosphorylation site. Images of parts of blood vessels and primitive canals at a higher magnification are depicted to the right.