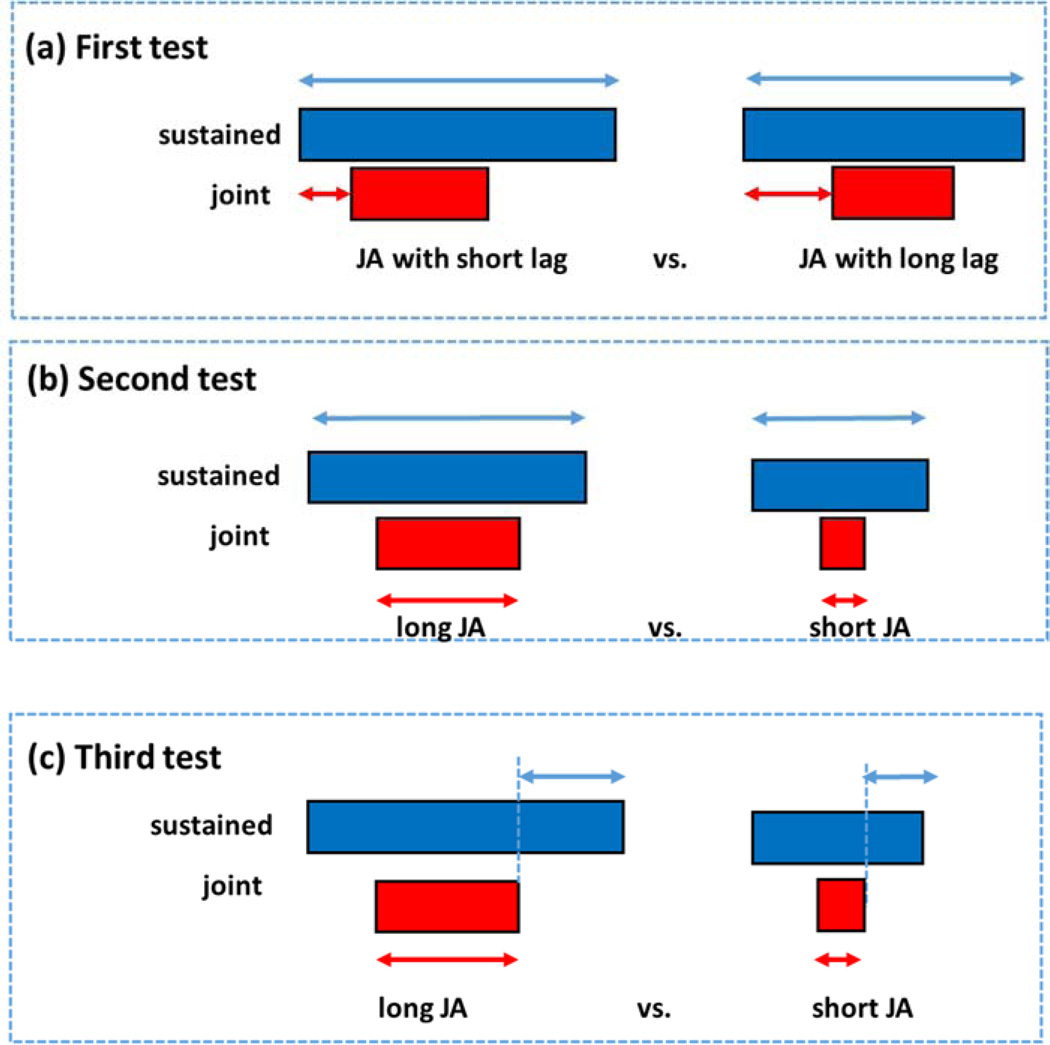
Figure 4.
Overview of data analysis to test three hypotheses. In all of the three cases, SA instances are divided into two groups based on the accompany JA instances (red arrows) and SA durations (blue arrows) in the two groups are compared. (a) SA instances are divided into SA instances with short-lag JA and those with long-lag JA. SA durations in the two groups show no significant difference. (b) SA instances are divided based on JA duration, and the results show that longer JA is associated with longer overall sustained attention. (c) SA instances are divided again into long-JA and short-JA cases as in (b). Infant sustained attention to the target after JA ended is longer for longer JA periods than for shorter ones.