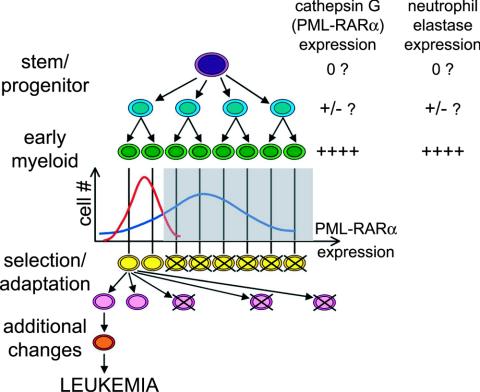
FIG. 7.
Model for the roles of PML-RARα dose and NE expression in APL penetrance. At the time when differentiating myeloid cells reach the stage of peak cathepsin G transgene activation (green cells), the population experiences a normal (stochastic) distribution of PML-RARα expression on a per-cell basis. Some earlier progenitor cells may also express very low levels of cathepsin G (i.e., PML-RARα) that may actually increase progenitor proliferation (see Discussion). Since the cathepsin G and neutrophil elastase genes are regulated in a similar fashion, NE expression should also occur in cells expressing PML-RARα. The low-expressing mCGPML-RARα model is represented by the red histogram, and the high-expressing hCG-PML-RARα transgenic model is represented by the blue histogram. In this model, cells expressing PML-RARα above a threshold level (gray box) experience toxicity, while the low expressers survive and expand to support the myeloid compartment. More cells in the mCGPML-RARα model fall within the survival window. Since the transformable progenitor pool is larger in these mice, they may be more likely to acquire the necessary adaptations or changes that predispose early myeloid cells to leukemic transformation, which is detected as a higher penetrance of disease.