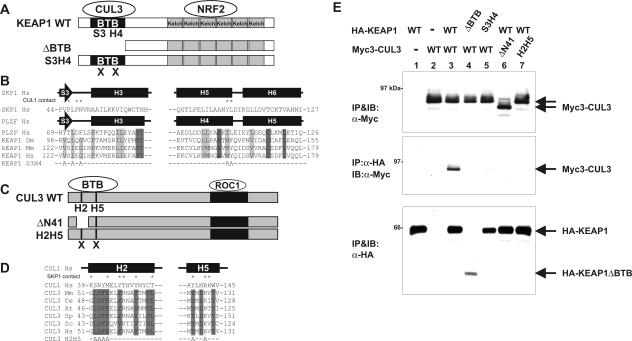
FIG. 3.
BTB domain in Keap1 binds to the N terminus of CUL3. (A) Schematic illustration of wild-type (WT) and mutant Keap1. (B) Conserved α/β-structure in BTB/POZ fold of SKP1, PLZF, and Keap1. Identical and conserved residues are indicated by dark gray and light gray shading, respectively. Residues in the SKP1 making contact with CUL1 are marked by asterisks. The mutated residues in the β-sheet S3 and α-helix H4 (KEAP1S3H4 mutant) are shown at the bottom. (C) Schematic figures of wild-type CUL3, ΔN41 (CUL3 in which the N-terminal 41 residues were deleted), and helix 2 helix 5 mutant (H2H5) CUL3. (D) Sequence comparison of helix 2 (H2) and helix 5 (H5) of CUL1 and CUL3. Residues in the H2 and H5 helices of CUL1 that make contact with SKP1 are marked by asterisks. Residues conserved in CUL3 are marked by shading. The residues mutated in the CUL3H2H5 mutant are shown at the bottom. (E) 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids expressing Myc-tagged CUL3 (Myc3-CUL3) or HA-tagged KEAP1 (HA-KEAP1) (wild-type [WT] or mutant CUL3 or KEAP1). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were lysed, and the CUL3-KEAP1 association was examined by IP-Western. IB, immunoblotting; α-Myc, anti-Myc antibody.