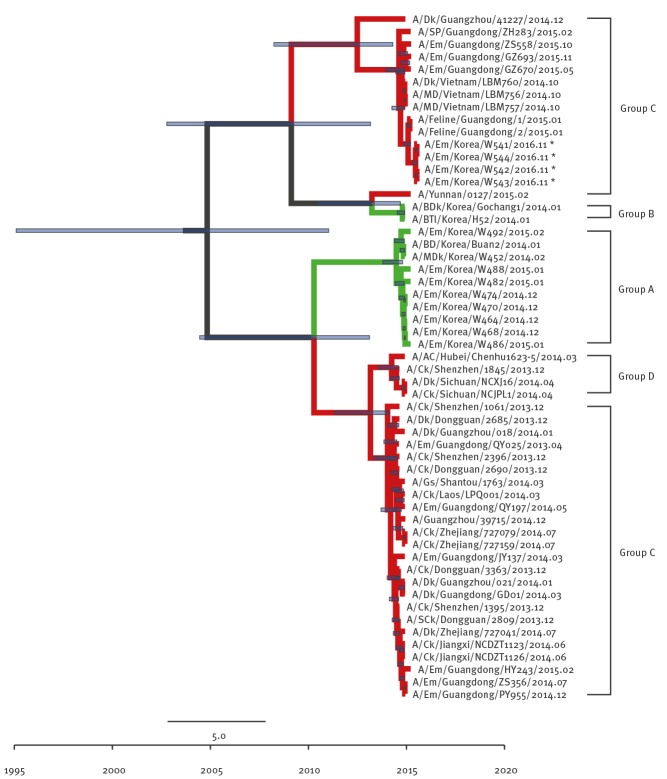
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of PB2 segment of novel H5N6 viruses, South Korea, November 2016
AC: anas crecca; BDk: breeder duck; BD: broiler duck; BTl: baikal teal; Ck: chicken; Dk: duck; Em: environment; GE, great egret; Gs, goose; MD, mallard; nt: nucleotide; PB: polymerase basic protein; SCk: silkie chicken; SP: syrrhaptes paradoxus.
To investigate the origins of novel H5N6 viruses (A/Em/Korea/W541/2016, A/Em/Korea/W542/2016, A/Em/Korea/W543/2016, and A/Em/Korea/W544/2016: marked with asterisks), full-length nt sequences of each segment were compared with available H5Nx and high blast scoring virus sequences from the GenBank. The deposited GenBank accession numbers of PB2 genes are KY273025-KY273028. Time-scaled phylogenies (dates shown on the horizontal axis) were inferred using strict-clock Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo analysis. Times of most recent common ancestors with 95% highest posterior density intervals are shown by the horizontal bars at each node (violet line). The month of isolation is indicated at the end of the viral nomenclature. The green line indicates the H5N8 subtype while the red line indicates the H5N6 subtype.