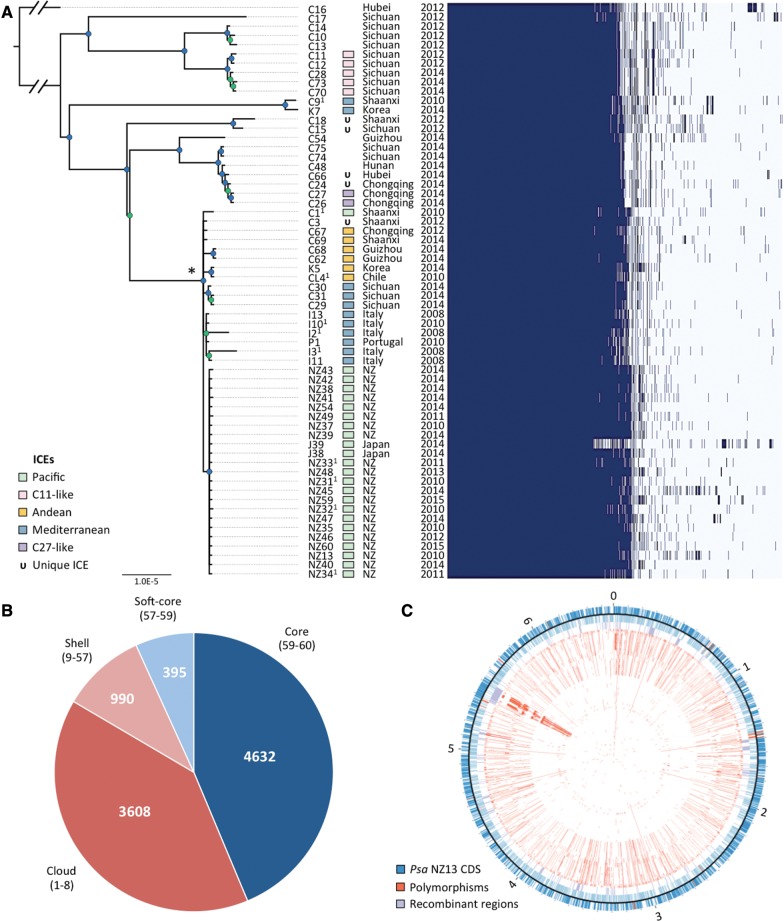
Fig. 2.—
Phylogeny of Psa-3. (A) RaxML Maximum likelihood tree based on 4,853,155bp nonrecombinant core genome alignment including 1,948 variant sites. FigTree was used for phylogeny visualization. All nodes displayed have bootstrap support values above 55% (55–80% in green, 81–100% in blue). The asterisk denotes the pandemic lineage. Integrative and conjugative element (ICE) presence; province (China) or country and year of isolation shown at right, followed by presence/absence matrix of all core and accessory genes. (B) The core and flexible genome of Psa-3. Parenthetical numbers represent the number of strains in the core, soft-core, shell, and cloud genomes. (C) Polymorphisms and recombinant regions mapped onto Psa NZ13 reference genome using CIRCOS (Krzywinski et al. 2009). Psa NZ13 CDS are displayed in the first and second ring (blue), with annotated Type 3 secretion system and effectors highlighted (red). Inner rings display polymorphisms in Psa-3 genomes ordered from most to least divergent relative to Psa NZ13. The most polymorphic region corresponds to the location of the integrative and conjugative element (ICE) in Psa NZ13.