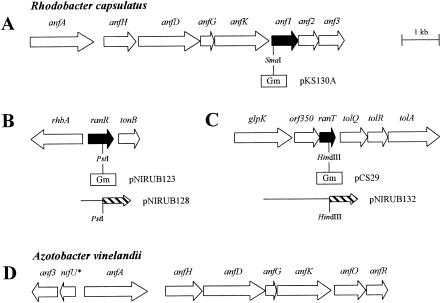
FIG. 1.
Organization of anf and ran genes involved in nitrogen fixation via the iron-only nitrogenases in R. capsulatus (A to C) and A. vinelandii (D). The locations and sizes of genes are given by arrows carrying their respective gene designations. The A. vinelandii nifU* gene is predicted to code for a truncated NifU protein in addition to the full-length nifU gene forming part of the nifUSV operon. Black arrows emphasize the R. capsulatus anf1 gene and two genes coding for Anf1 interactors. Below these genes, the locations of interposon cassettes ([Gm], gentamicin resistance) are shown. Hybrid plasmids pKS130A, pNIRUB128, and pNIRUB132, used to create anf1, ranR, and ranT mutant strains, respectively, are based on mobilizable narrow-host-range plasmids (Table 1). Hybrid plasmids pNIRUB128 (ranR-lacZ) and pNIRUB132 (ranT-lacZ) are based on the mobilizable broad-host-range plasmid pML5. The [Gm] interposon and the lacZ gene (hatched arrow) are not drawn to scale.