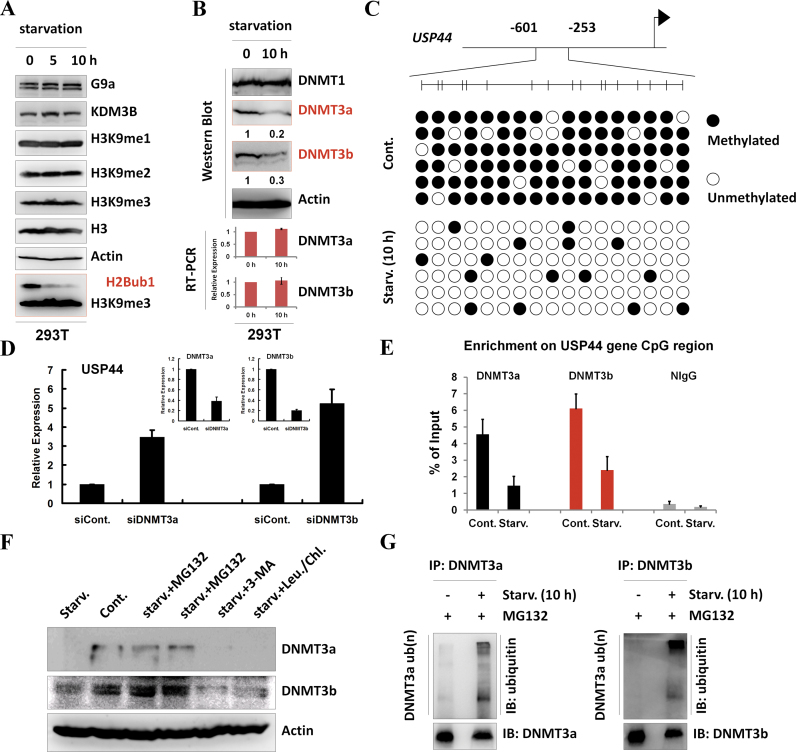
Figure 3.
Starvation-induced USP44 up-regulation is mediated by DNA methylation. (A) 293T cells were starved by treating with HBSS for the indicated periods. Cell extracts were then prepared and subjected to western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. The experiments were repeated more than three times (n > 3). (B) 293T cells were treated with or without starvation for 10 h by incubating with HBSS. Protein extracts and total RNA were then prepared and subjected to western blot and RT-PCR analyses usingspecific antibodies and primers,as indicated. The experiments were repeated more than three times (n > 3). (C) Methylation of the USP44 gene is decreased in response to starvation. DNA methylation profiling analysis was employed in control and HBSS-starved 293T cells. The detailed procedure was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions (Millipore, Lot#: 17-10451). (D) 293T cells were transfected with a control or a DNMT3a- or DNMT3b-specific siRNA for 48 h. The total RNA was then isolated and subjected to RT-PCR analysis using the indicated primers. At least three biological replicates were analyzed (n > 3). (E) 293T cells were treated with or without starvation for 10 h. The cells were then lysed and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay using antibodies against DNMT3a and DNMT3b or normal control IgG (as a negative control), followed by real-time PCR with specific primers for the USP44 gene CpG region, as indicated. At least three biological replicates were analyzed (n > 3). (F) 293T cells were treated with starvation or starvation together with MG132 (25 μM), 3-MA (10 mM) or chloroquine (100 μM) and leupeptin (50 μM) for 10 h. The cells were then lysed and subjected to western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. The experiments were repeated three times (n = 3). (G) In vivo ubiquitination assays were performed in control and HBSS-starved 293T cells together with MG132 incubation. The immunoprecipitation was performed under denaturing conditions using antibodies against DNMT3a and DNMT3b, followed by western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. The experiments were repeated three times (n = 3).