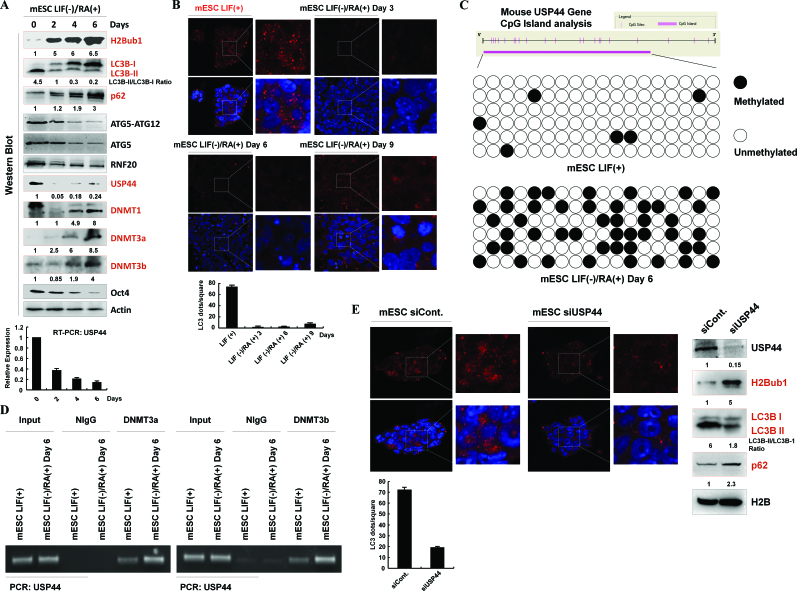
Figure 6.
H2Bub1 correlates with the autophagy activity in mESCs and the differentiation of mESCs. (A) H2Bub1 levels correlates with autophagy in mESCs and their differentiation. mESCs were cultured with RA (RA(+)) and without LIF (LIF(−)) for different periods and were lysed for western blot analysis using different antibodies, as indicated. The experiments were repeated more than three times (n > 3). (B) Autophagosomes in mESCs and differentiated mESCs. mESCs and mESCs cultured with RA (RA(+)) and without LIF (LIF(−)) for different periods were subjected to immunostaining analysis using anti-LC3B antibody. DAPI was used to detect the cell nucleus. (C) Methylation of the mouse USP44 gene is increased after mESC differentiation. DNA methylation profiling analysis was employed in control and differentiated mESCs. The detailed procedure was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions (Millipore, Lot#: 17-10451). (D) Control and differentiated mESCs were lysed and subjected to a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay using antibodies against DNMT3a and DNMT3b or normal control IgG (as a negative control), followed by PCR with specific primers for USP44, as indicated. The experiments were repeated more than three times (n > 3). (E) USP44 regulates autophagy in mESCs. Control siRNA- and USP44-specific siRNA-transfected mESCs were subjected to immunostaining analysis using an anti-LC3B antibody, or subjected to western blot assays with antibodies as indicated. DAPI was used to detect the cell nucleus. The experiments were repeated more than three times (n > 3).