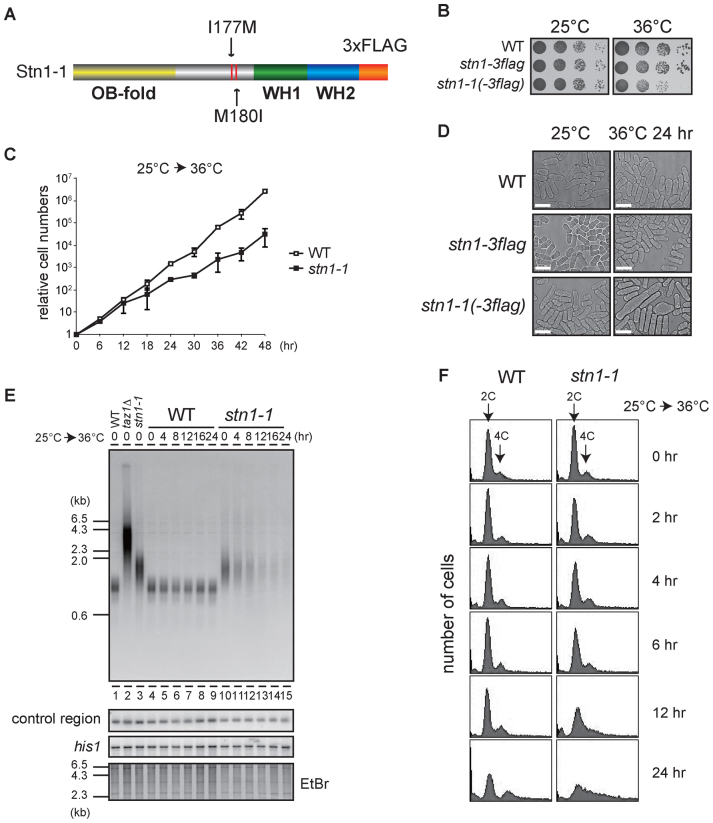
Figure 1.
Loss of telomeres at high temperature in temperature-sensitive stn1-1 mutant yeast. (A) The domain structure of Stn1-1. Positions of I177M and M180I substitutions are indicated. (B) Ten-fold serial dilutions were spotted onto YES plates and incubated at 25°C and 36°C for 3 days. (C) Growth curves of wild-type and stn1-1. Wild-type (JK317) and stn1-1 were cultured at 25°C in liquid YES medium and the temperature was shifted to 36°C for 48 h. Cell numbers were counted every 6 h. (D) Micrographs of WT, stn1-3flag, and stn1-1 obtained with a phase-contrast optical microscope (DeltaVision Elite). The scale bar represents 10 μm. (E) Wild-type, taz1Δ, and stn1-1 were cultured at 25°C (lanes 1–3). Wild-type and stn1-1 were cultured at 36°C for the indicated times (lanes 4–15). EcoRI-digested genomic DNA fragments were analyzed by Southern hybridization with a telomeric probe to detect both G- and C-strand telomere DNAs. The same membrane was re-hybridized with a probe specific to an interior region of chromosome II (control region) and the his1 gene locus (see Materials and Methods). The EtBr-stained gel was photographed before blotting. (F) Wild-type and stn1-1 cultured in YES at 36°C for the indicated times were stained with Propidium Iodide (PI) and analyzed with FACS.