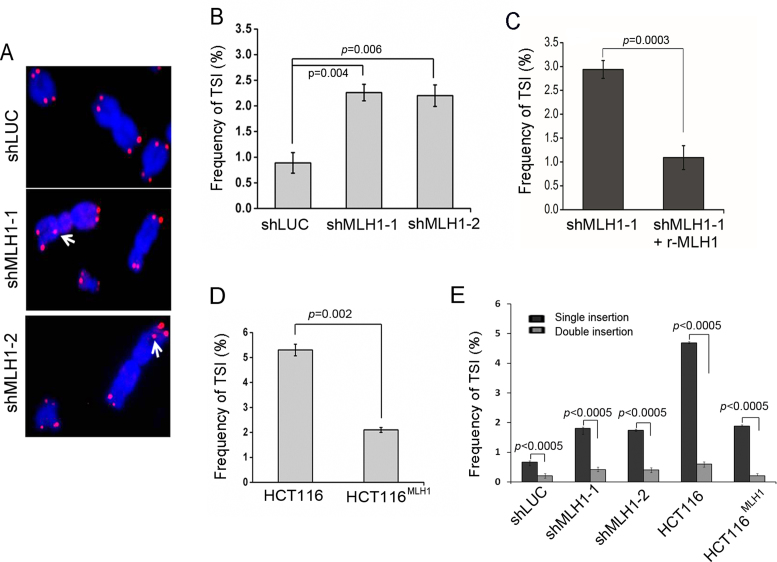
Figure 2.
MLH1 suppression induces TSI at non-telomeric sites. (A) Metaphase chromosomes from MLH1 suppressed HeLa cells (8 days after puromycin selection) were hybridized by telomeric probe. Representative FISH images are shown. White arrow points to inserted telomeric sequences at intra-chromosomal loci. (B) Frequency of TSI (expressed as % chromosomes with inserted telomere sequences) in HeLa shMLH1 and control shLUC cells. Two tailed t-test was used to calculate statistical significance in all data presented in this manuscript unless state otherwise. Error bars are SEM in all experiments shown in this manuscript. (C) Frequency of TSI after rescuing MLH1 knockdown. RNAi-resistant wild-type MLH1 was expressed in HeLa cells, followed by shRNA expression to knockdown endogenous MLH1. TSI was detected by FISH. (D) Frequency of TSI in HCT116 cells and HCT116MLH1. (E) Percentage of TSI events appearing on a single sister chromatid (single insertion) vs TSI in two sister chromatids (double insertion). In each experiment, >1500 chromosomes from each sample were analyzed and each experiment was repeated with three independent replicates.