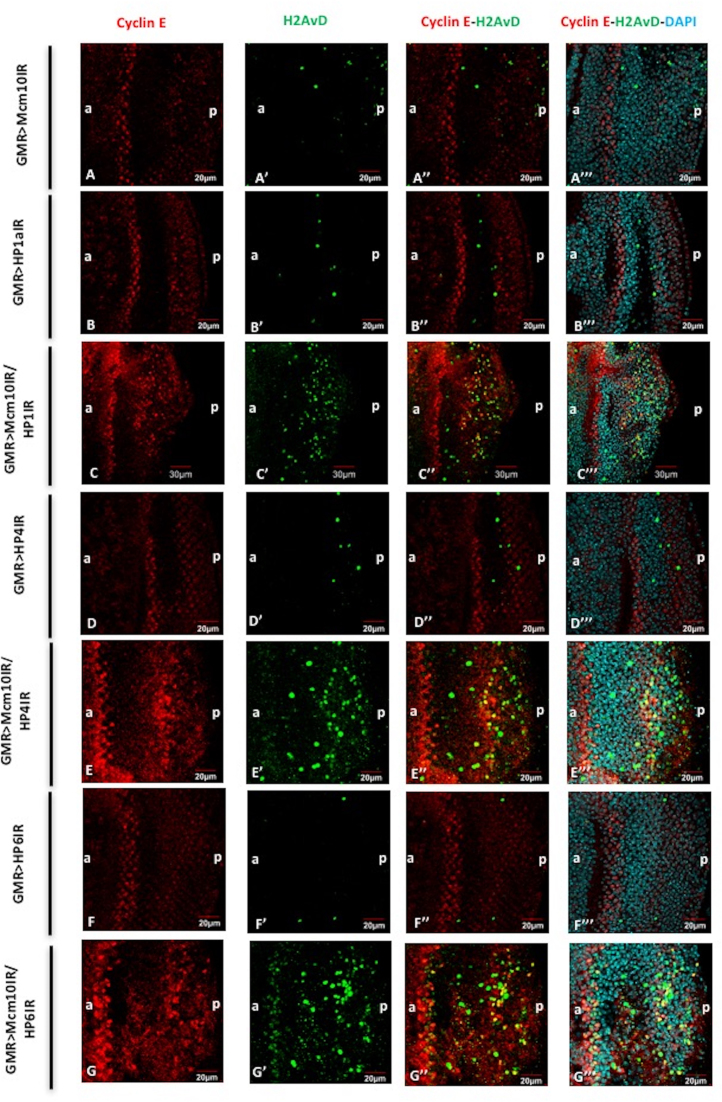
Figure 9.
Mcm10 and HP1a, HP4, HP6 play roles in G1-S cell cycle checkpoint. Eye imaginal discs from GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-Mcm10IR/+; + (A–A’’’), GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-HP1a73-181IR/+ (B–B’’’), GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-Mcm10IR/+; UAS-HP1a73-181IR/+ (C–C’’’), GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-HP4IR/+ (D–D’’’); GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-Mcm10IR/+; UAS-HP4IR/+ (E–E’’’), GMR-GAL4/+; +; UAS-HP6IR/+ (F–F’’’), GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-Mcm10IR/+; UAS-HP6IR/+ (G–G’’’) flies were immunostained with anti-Cyclin E (red) and anti-H2AvD (green). All of the discs were stained with DAPI for DNA staining (blue). (A–A’’’) the number of Cyclin E-positive cells was not changed in the eye imaginal discs of Mcm10 RNAi lines. However, eye imaginal discs from double knockdown of Mcm10 and HP1a (C–C’’’), Mcm10 and HP4 (E–E’’’), and Mcm10 and HP6 (G-G’’’) show significantly increased both Cyclin E-positive and phospho-H2AvD-positive cells in posterior regions. Furthermore, some of the phospho-H2AvD-positive cells were merged with Cyclin E-positive cells (C’’, E’’ and G’’) likely representing for cells arrested in G1-S checkpoint. In contrast, we could not find the same phenotypes in the single knockdown of these genes (A’’, B’’, D’’ and F’’). The flies were reared at 28°C. Scale bars indicate 20 or 30 μm. (a) Indicates anterior, (p) indicates posterior.